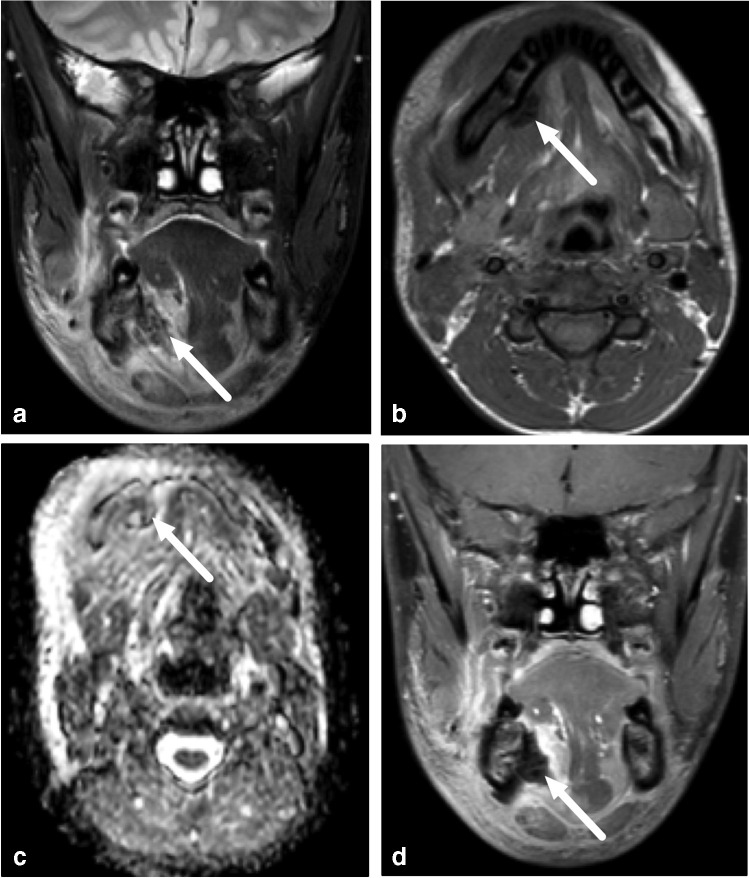
Fig. 7.
False-negative abscess in a 13-year-old boy with an odontogenic infection. Imaging was done after removal of the infected d46 tooth and incision of an abscess. Coronal fat-saturated T2-weighted (a) and axial T1-weighted (b) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images demonstrate extensive soft-tissue edema, and a relatively T2 and T1 hypointense subperiosteal collection (arrows). Axial apparent diffusion coefficient images (c) and post-contrast coronal fat-saturated T1-weighted images (d) show no restricted diffusion or contrast enhancement (arrows). This heterogeneous subperiosteal collection was considered to contain postoperative gas and/or blood with no clear evidence of a residual abscess. Yet, purulence was found at surgery