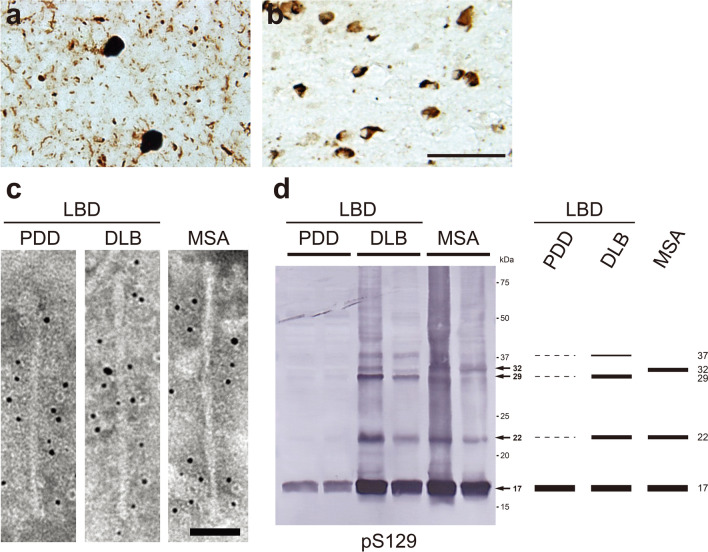
Fig. 2.
Ultrastructural and biochemical characterization of pathogenic α-syn extracted from human synucleinopathies. Immunohistochemistry of brain section from patients with synucleinopathies, stained with pS129 antibody. a Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in DLB. b Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in MSA. Scale bar, 50 μm. c Immunoelectron microscopy of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions extracted from brains of synucleinopathy patients. Electron micrographs show fibrous structures with 5–10 nm in diameter positive for pS129, after labeling with secondary antibody conjugated to 5 nm gold particles. Straight filaments in LBD (PDD and DLB), and twisted filaments with 80–100 nm periodicity in MSA were observed. Scale bar, 50 nm. d Immunoblot analyses of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions prepared from brains of synucleinopathy patients. Sarkosyl-insoluble phosphorylated α-syn (17 kDa) was detected with pS129 antibody. Disease-specific high-molecular-weight α-syn species were also observed: 22, 29, and 37 kDa bands in LBD (PDD and DLB), and 22 and 32 kDa bands in MSA. All data are original for this review