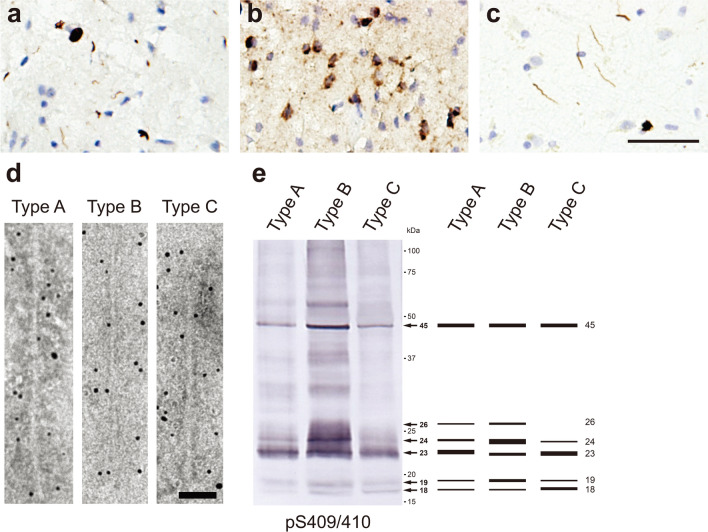
Fig. 3.
Ultrastructural and biochemical characterization of pathogenic TDP-43 extracted from human TDP-43 proteinopathies. Immunohistochemistry of brain section from patients with TDP-43 proteinopathies, stained with pS409/pS410 antibody. a Neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (NCIs) and short degenerative neurites (DNs) in FTLD-TDP Type A. b NCIs in FTLD-TDP Type B. c Long DNs in FTLD-TDP Type C. Scale bar, 50 μm. d Immunoelectron microscopy of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions extracted from FTLD-TDP (type A, type B, type C) patients. Electron micrographs show fibrous structures with 10–15 nm in diameter positive for pS409/pS410, after labeling with secondary antibody conjugated to 5 nm gold particles. Scale bar, 50 nm. e Immunoblot analyses of sarkosyl-insoluble fractions prepared from brains of patients withTDP-43 proteinopathies. Sarkosyl-insoluble phosphorylated TDP-43 (45 kDa) was detected with pS409/410 antibody. Subtype-specific C-terminal fragments were also observed: 18, 19, 23, 24 and 26 kDa bands in type A, 18, 19, 23, 24 and 26 kDa bands in type B, 18, 19, 23 and 24 kDa bands in type C. All data are original for this review