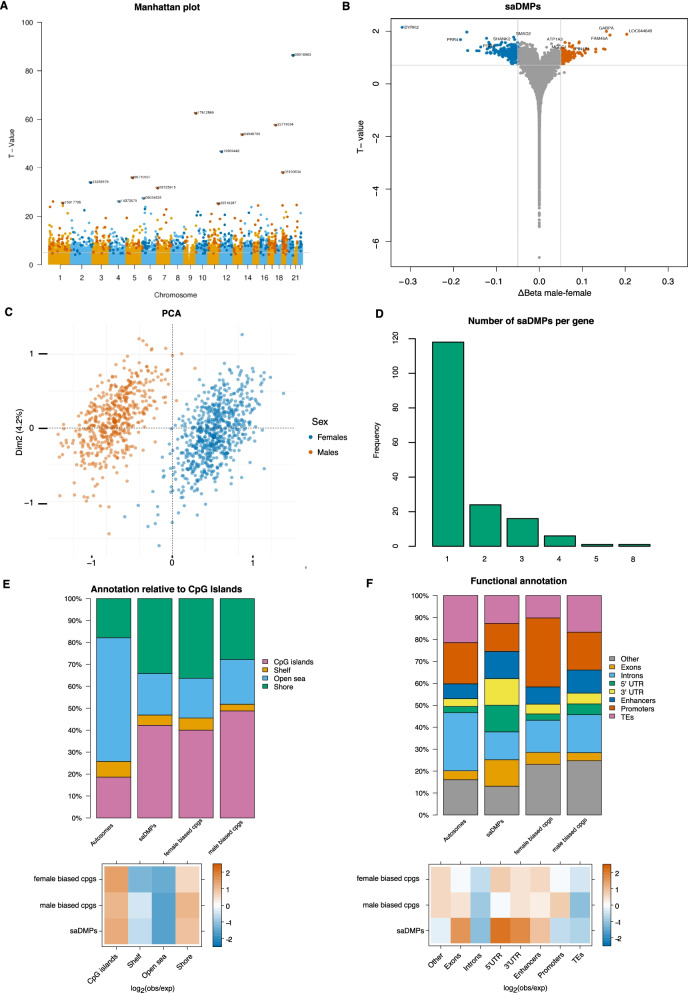
Fig. 1.
Location and characterisation of saDMPs. A Manhattan plot for EWAS analysis of sex. CpG sites which met a threshold of FDR < 0.05 and had an average beta change of > 0.05 and found in both discovery and validation data sets were considered significant and are represented by darker colours. B Volcano plot for saDMPs. CpGs which are not significant in both the discovery and validation data sets are represented in grey, replicated saDMPs male-biased CpGs are in orange and replicated saDMPs female-biased CpGs in blue. Grey points displayed beyond the cut off points represent CpG sites which were met the criteria in the discovery data set (FDR < 0.05 and deltaBeta value > than 0.05 in any direction) but were not replicated in the validation data set. C Principal component analysis of beta values at the significant saDMPs. Male samples are indicated in orange while female samples are indicated in blue. D Number of saDMPs harboured by individual genes. E Top panel shows the annotation of all saDMPs (n = 396), female-biased CpGs (n = 293) and male-biased CpGs (n = 103) relative to CpG island regions compared to the autosomal background. Bottom panel shows the log2 (obs/exp) annotations based on the autosomal background of the different annotations. F Top panel shows the overlap of all saDMPs (n = 396), female-biased CpGs (n = 293) and male-biased CpGs (n = 103) with genomic features compared to the autosomal background. Bottom panel shows the log2 (obs/exp) annotations based on the autosomal background of the different annotations