FIGURE 6.
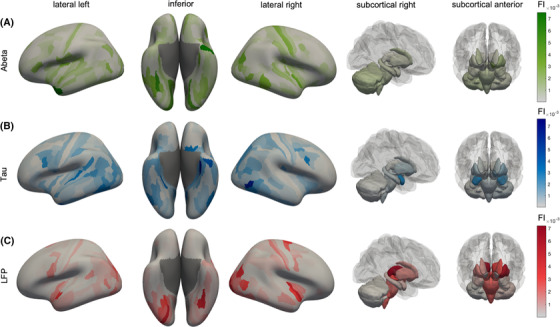
Anatomical representation of feature importance (FI) distribution. Displayed are cortical regions from left, right, and inferior as well as subcortical regions. The color indicates the FI. A, Aβ FI. The anatomical patterns reveal high importance of left‐temporal regions, as well as the left dorsal stream in the parietal and occipital cortex. The Aβ top features showed a more disseminated allocation mostly in the temporal, occipital, frontal, and insular cortices, which is also in line with typical amyloid deposition and locations of increased AV‐45 uptake in AD. 43 B, Tau features show a similar pattern as Aβ, but with a higher focus on typical Braak stage 1 regions (as the entorhinal cortex). Most of the tau top features can be allocated to the temporal lobe, which is also the location of early tau deposition according to the neuropathological Braak and Braak stages I–III 41 , 44 and the location of increased in vivo binding of 18F‐AV‐1451 in AD. 45 In particular, the entorhinal cortex is a consistent starting point of the sequential spread of tau through the brain 44 , 45 and also showed the most robust relationship between flortaucipir and memory scores in a recent machine learning study. 46 C, Simulated frequencies do not show strong laterality as the empirical features but seem to have a focus in both occipital lobes, where typically alpha oscillations occur. The occipito‐temporal and occipito‐parietal regions of the first area are typical alpha‐rhythm generators in resting‐state electroencephalogram. 47 Alteration of these posterior alpha sources is a typical phenomenon in AD and MCI compared to HC. 48 The ventral or “what” stream and the dorsal or “where” stream have been implicated in object recognition and spatial localization and are essential for accurate visuospatial navigation. 49 Impairment in visuospatial navigation is a potential cognitive marker in early AD/MCI that could be more specific than episodic memory or attention deficits. 50 Besides this, subcortical areas like the thalami play a more crucial role than for Aβ and tau. Aβ, amyloid beta; AD, Alzheimer's disease; FI, feature importance; HC, healthy controls; MCI, mild cognitive impairment
