Figure 4. Balance of pro-regenerative and mechano-inflammatory responses in articular cartilage with abnormal mechanical load.
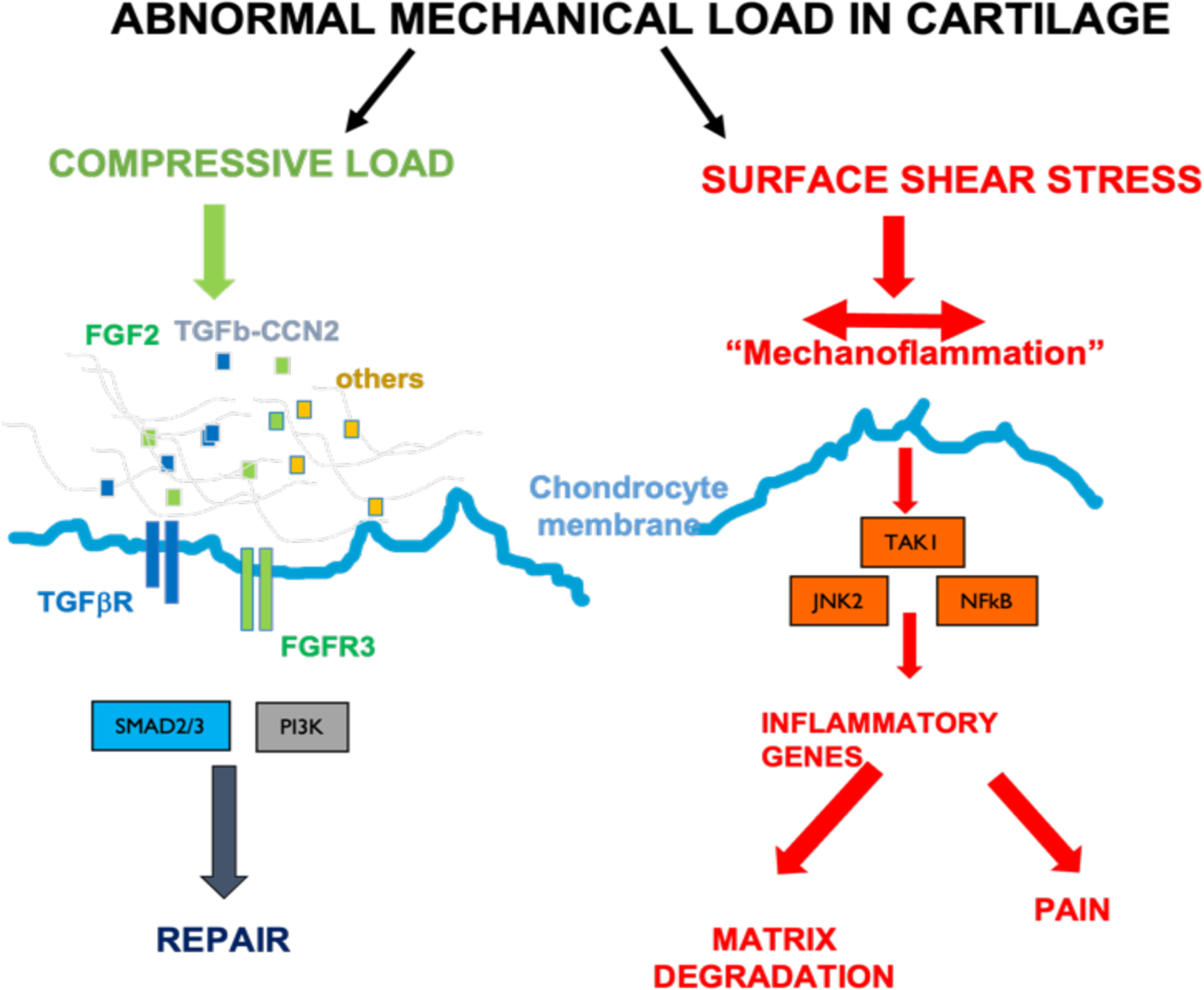
Compressive load leads to sodium dependent release of pericellular matrix growth factors, which drive repair and chondroprotection through a variety of intracellular signalling pathways. Surface shear stress (perpendicular to compressive load) leads to activation of TGFβ-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) dependent inflammatory signalling and results in nerve growth factor regulation (driving pain) and matrix degradation.
