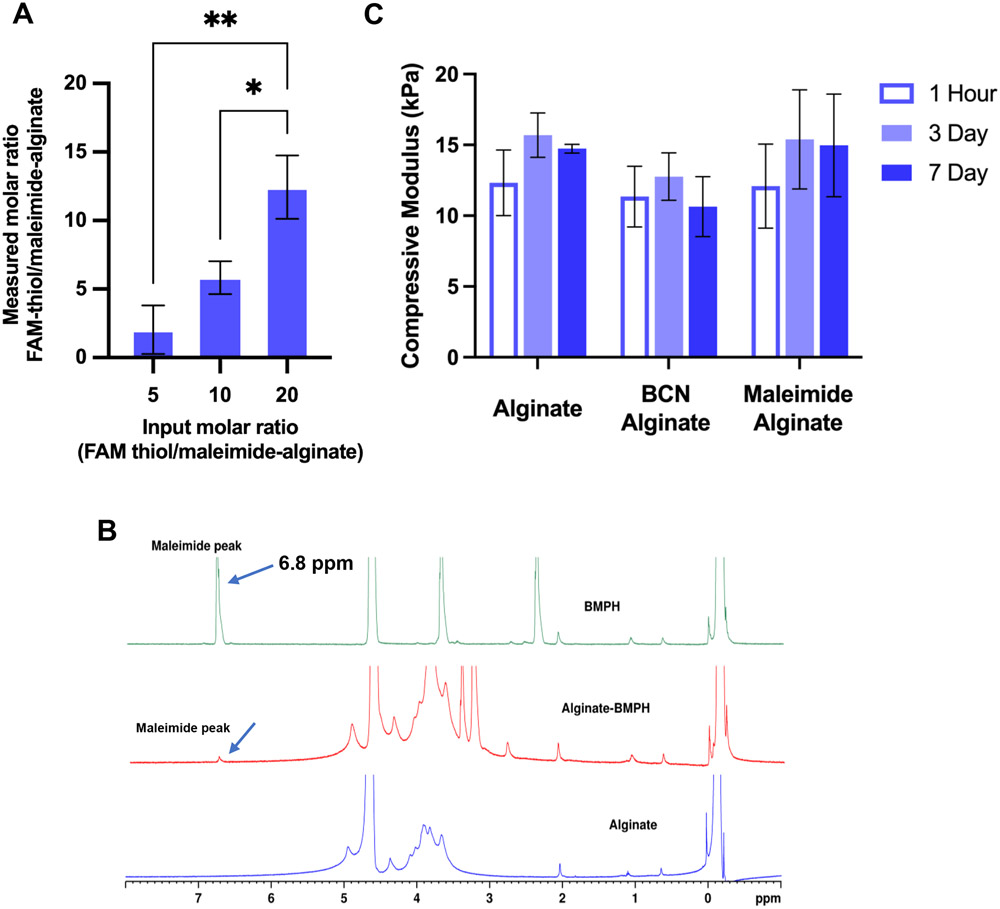
Figure 2. Quantification of peptide conjugation efficiency using maleimide–thiol reaction and mechanical property of modified alginate.
A) Conjugation of FAM-thiol to maleimide-alginate (1% w/v) at three different input molar ratios (5, 10, and 20) via Maleimide-thiol click reaction between cysteine and BMPH. FAM-thiol was used as a surrogate for AG73. Fluorescence of the final product was measured to determine the molar ratio of FAM-thiol to maleimide-alginate at the different molar inputs. ~55% coupling efficiency was observed. Error bars are ±SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison's test. B) 1H NMR plots of substituted BMPH–alginate (red) with input BMPH molar ratio 10 (final DS: 5) shows the presence of characteristic peaks of maleimide groups at 6.8 ppm (solid arrow) when compared to unmodified alginate (blue) and pure BMPH (green). C) Modification to the backbone of alginate chain and pre-incubation times with media do not impact modulus. Error bars are ±SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison's test was used to compare the modulus within individual polymer condition pre-incubated at three different time points and to compare modulus between modified alginate hydrogels.