Figure 2. The ECD module defines activation triggers and diversifies sensor functions.
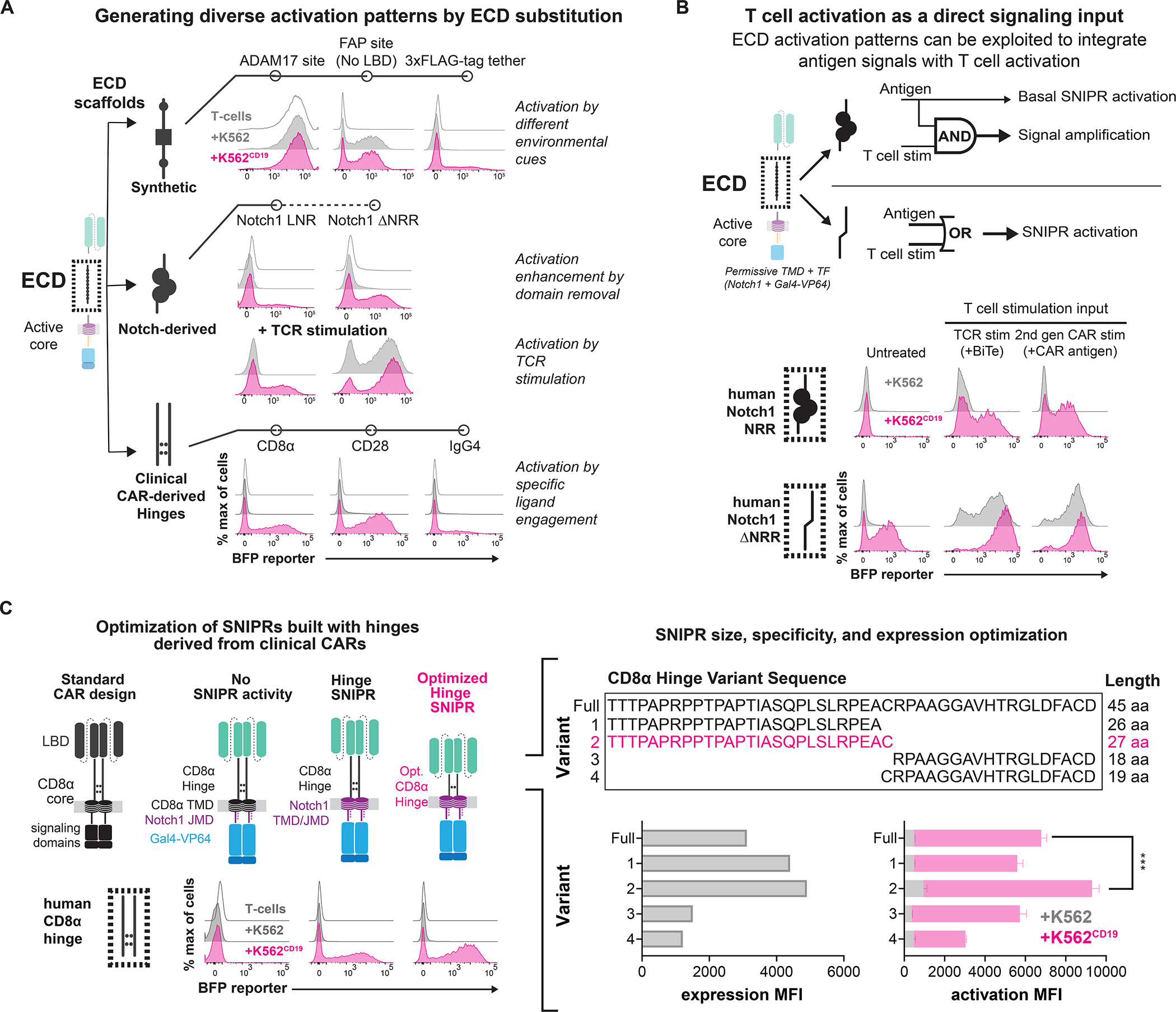
(A) SNIPR ECDs with exposed cleavage sites display ligand-independent signaling. Deleting the NRR from synNotch produces a receptor that is sensitive to both ligand and TCR stimulation. A variety of hinge domains utilized in CARs also demonstrate ligand-dependent signaling. (B) Same as A, but with two methods of T cell stimulation. A SNIPR with the Notch1 NRR core domain displays enhanced activation with a Bi-specific T cell Engager (BiTE) targeting a K562 antigen, and a co-expressed second-generation CAR targeting a separate antigen. A SNIPR with a truncated Notch1 NRR activates with these stimuli independent of the presence of ligand. (C) Same as A, but with variations of the CD8α Hinge. The CD8α Hinge can be optimized to enhance SNIPR expression and activation. Statistics were calculated using unpaired T-tests, ***P≤0.001.
