Figure 3. Transmembrane and juxtamembrane domain libraries enable modular assembly of SNIPR architectures.
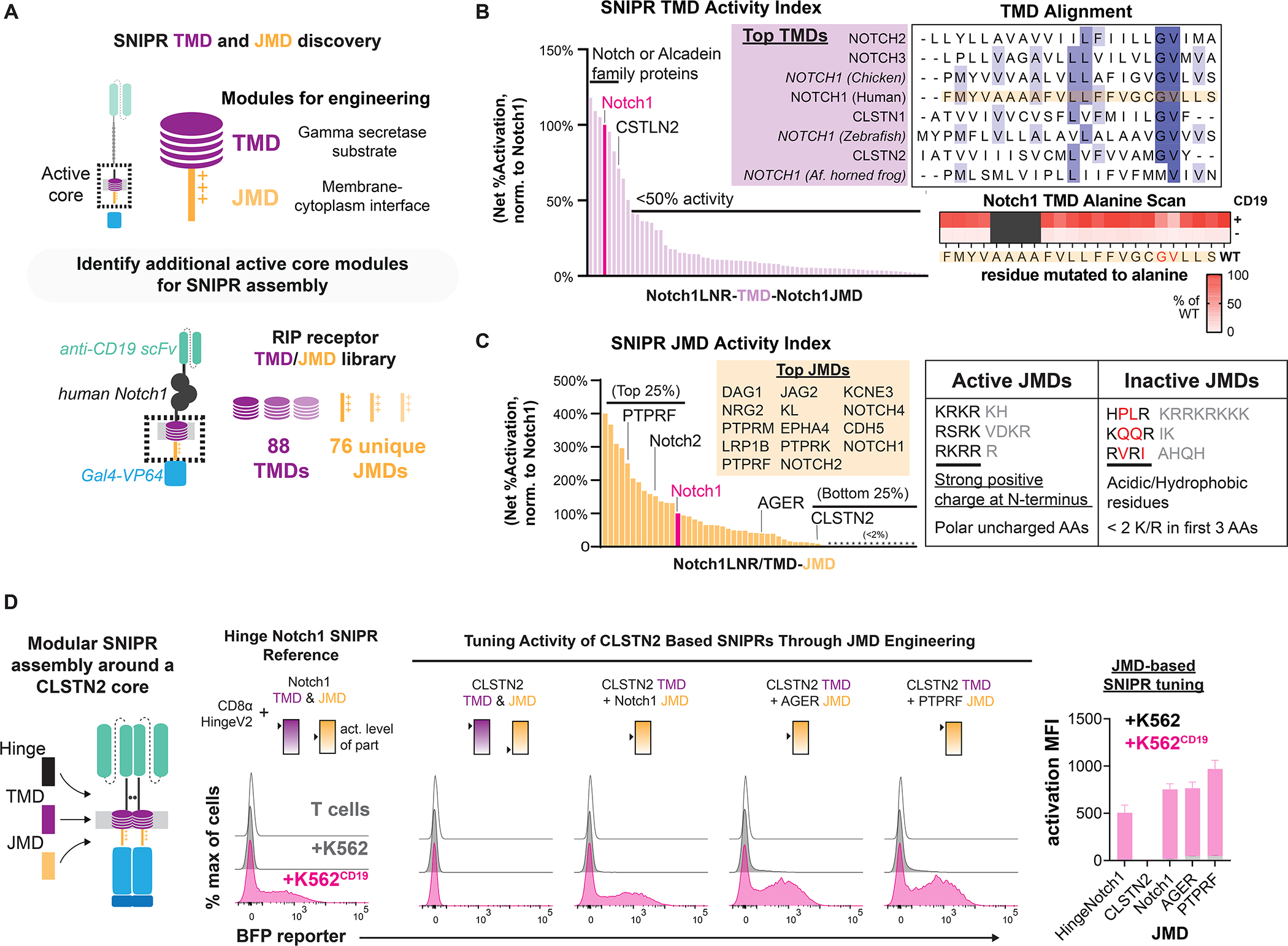
(A) To identify functional receptor TMDs and JMDs for modular assembly, 88 TMDs and 76 JMDs were cloned into a human synNotch scaffold, replacing either the Notch1 TMD or JMD, respectively. Jurkat T cells expressing an inducible BFP reporter were transduced with these SNIPR libraries in an arrayed format. (B) Normalized results of TMD screening in Jurkat T cells. An alignment of the best performing TMDs shows a common Gly-Val motif (Dark blue = >80% agreement with consensus sequence, blue = >60% agreement, light blue = >40% agreement). An alanine scan of the human Notch1 TMD in primary T cells supports the importance of this motif. (C) Same as B, but with the JMD library. High-performing JMDs are strongly basic at their N-termini and may include polar residues but not acidic or hydrophobic residues. (D) Compared to a reference SNIPR containing the Notch1 TMD/JMD, a SNIPR containing the CLSTN2 TMD/JMD is inactive, but receptor function is restored when the CLSTN2 JMD is replaced with the Notch1, AGER or PTPRF JMD.
