Figure 5. Humanization of SNIPRs to reduce immunogenicity potential for cell-based therapies.
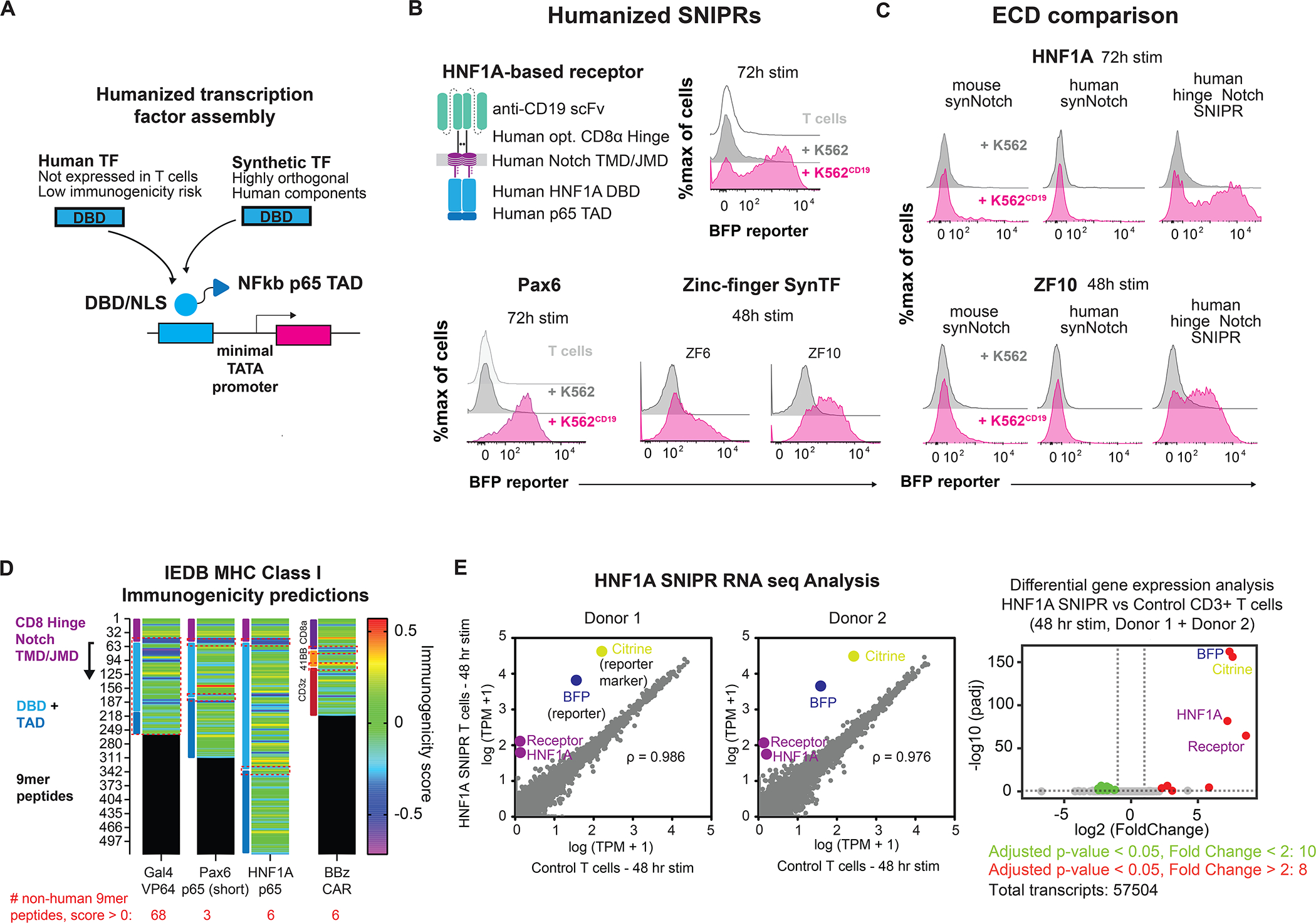
(A) Humanized TF and RE construction. (B) Activity of fully humanized SNIPRs. (C) SNIPR receptor scaffold compatibility with humanized TFs. (D) Assessing SNIPR immunogenicity. 9mer peptide sequences for SNIPRs with Gal4-VP64, Pax6, and HNF1A transcription factors were assessed for MHC I immunogenicity. Relative immunogenic potential across receptors was examined by comparing immunogenicity scores in regions derived from non-contiguous human protein sources (highlighted in red dashed boxes). Average scores: Pax6 0.039, HNF1A 0.156, BBz 0.102. (E) HNF1A SNIPR RNA-sequencing analysis. HNF1A SNIPR T cells were induced with target cells for 48 hours and sorted to remove targets for RNA-sequencing analysis. Correlation of transcriptomes against non-SNIPR T cells in two donors show few differences apart from SNIPR circuit components. Pearson correlation coefficients (left panel) were calculated for native transcripts (gray). Differential gene analysis shows few upregulated or downregulated genes compared to control cells following circuit induction (right panel).
