Figure 7. Design framework for next generation synthetic receptors for custom transcriptional regulation in therapeutic cells.
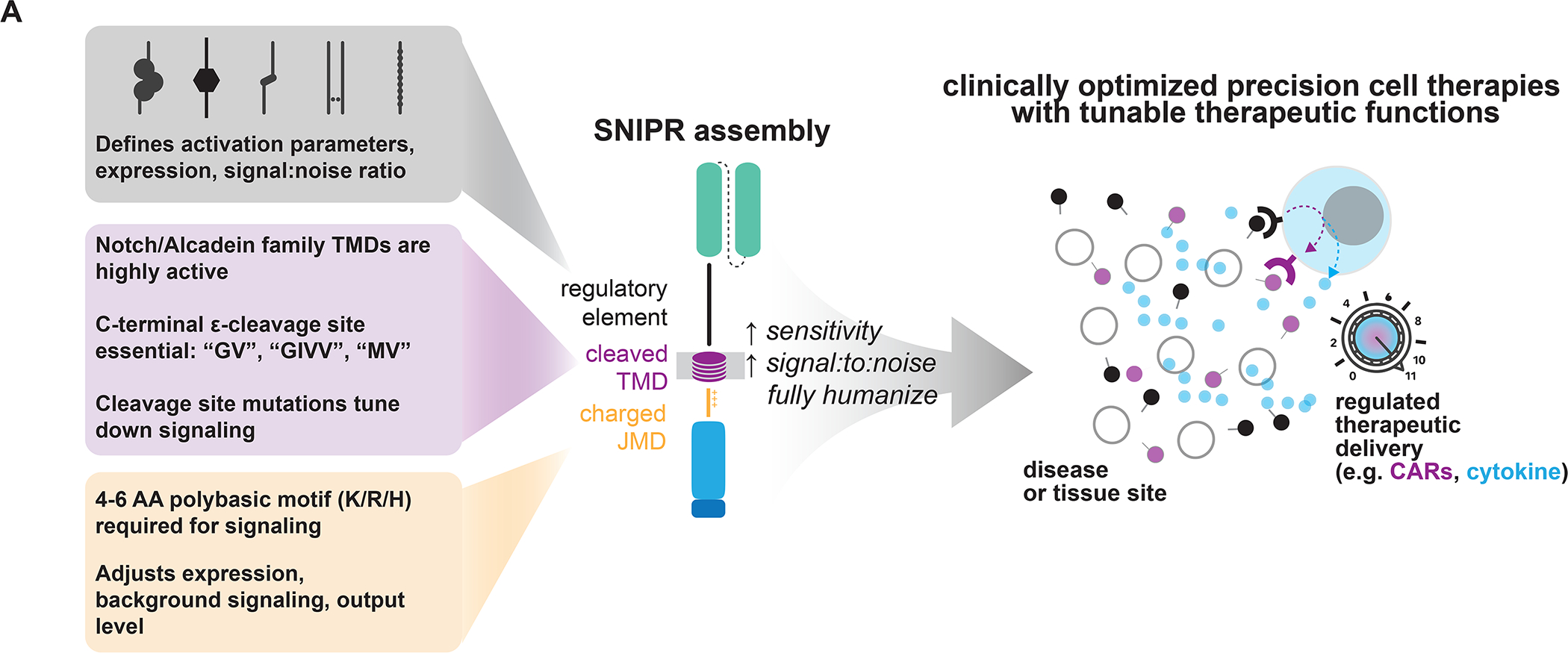
SNIPRs can be built through design of the receptor ECD, TMD, and JMD. The receptor ECD represents the first regulatory site and affects receptor activation parameters, expression, and stringency for ligand. Several known C-terminal motifs in the receptor TMD, commonly found in the Notch and Calsyntenin families, appear to be important for receptor signaling. Highly basic residues in the receptor JMD are required for signaling, and the choice of JMD can strongly affect receptor expression and output levels. By combining these elements, clinically relevant SNIPRs can be built that utilize fully human proteins and are compact, highly expressed, and regulatable. Our SNIPR design framework opens the possibility to build customized precision cellular therapeutics.
