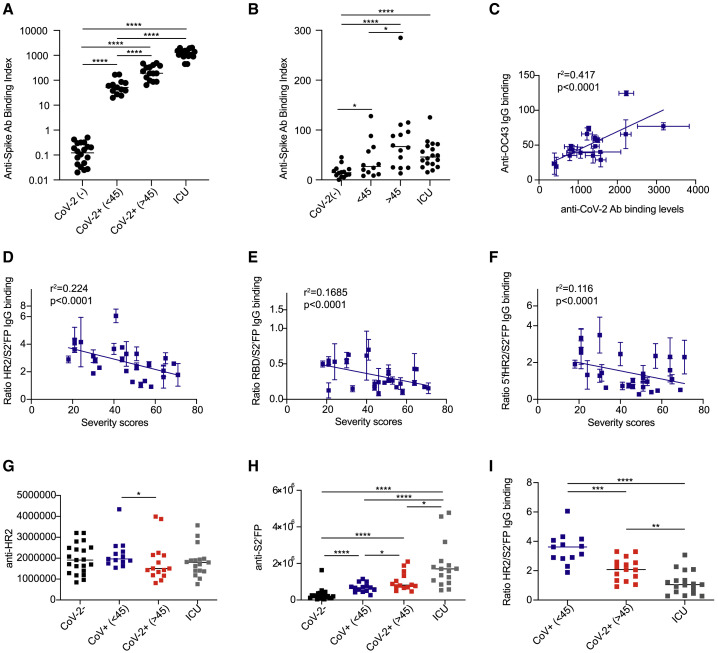
Figure 7.
The ratio of IgG targeting the HR2/S2′FP regions of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein correlates with COVID-19 severity in convalescent and ICU-hospitalized patients
(A and B) (A) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 or (B) anti-OC43 spike IgG titers as detected by CBA in SARS-CoV-2-naive (CoV-2−), non-hospitalized convalescent (CoV-2+), and ICU-hospitalized COVID-19 patients (n = 20 naive, 28 convalescent, and 17 ICU).
(C) Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 versus OC43 anti-spike IgG titers in ICU-hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
(D–F) The ratio of (D) HR2/S2′FP, (E) RBD/S2′FP, and (F) 5′fHR2/S2′FP in convalescent non-hospitalized donors.
(G and H) The levels of IgG binding to (G) HR2 and (H) S2′FP regions as detected by luminescent ELISA in SARS-CoV-2-naive (CoV-2−), convalescent non-hospitalized donors split by mild (<45), more severe (>45), and ICU-hospitalized COVID-19 patients.
(I) The ratio of HR2/S2′FP IgG-binding levels in SARS-CoV-2-convalescent donors versus ICU-hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The SEMs of N = 3 experiments are shown.