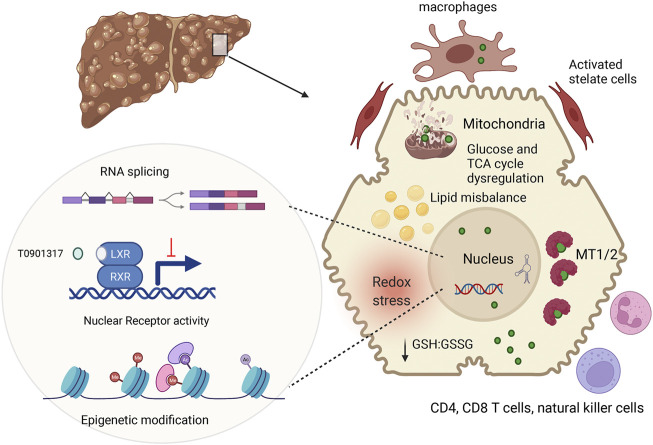
FIGURE 2.
Summary of main pathologic changes in WD liver. ATP7B mutations result in hepatic accumulation of copper (green circle). In the cytosol, Cu is sequestered by metallothioneins (MT1/2), whereas excess Cu causes glutathione oxidation (lower GSH:GSSG ration), contributing to redox stress. Cu elevation in nuclei, alters RNA processing, including splicing (Burkhead et al., 2011) inhibits NR function and induces epigenetic changes. Downstream effects include dysregulation of metabolic profiles in hepatocytes. Hepatocyte injury and possibly Cu accumulation in non-parenchymal cells stimulates immune cells and stellate cells, resulting in inflammation and fibrosis. The figure was generated using BioRender.