Figure 1.
Characterization of HiBiT-tagged tau assemblies and their entry into the cytosol of HEK293 cells
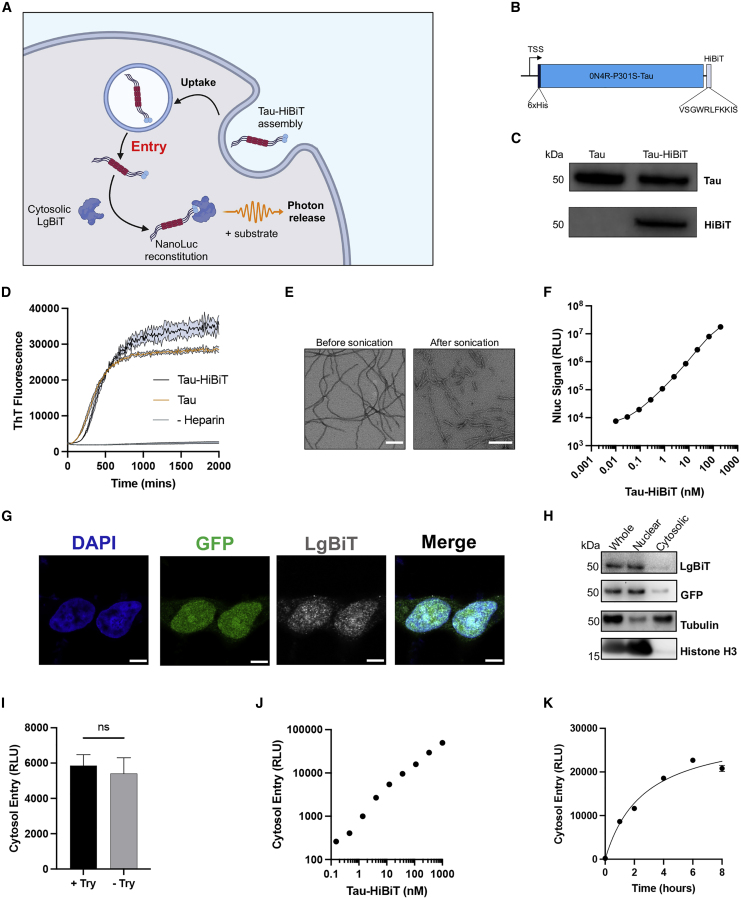
(A) Cartoon depicting the intracellular reconstitution of Nluc and the enzymatic production of light through interaction of exogenously supplied assemblies of tau-HiBiT with intracellular LgBiT.
(B) Depiction of the His6-0N4R-P301S-Tau-HiBiT construct and the amino acid sequence of the HiBiT peptide.
(C) Western blot of 50 ng recombinant tau or tau-HiBiT monomers with anti-tau (Dako) or anti-HiBiT antibody.
(D) Time course of 5 μM tau-HiBiT and tagless tau aggregation kinetics monitored by thioflavin T (15 μM) fluorescence; n = 4.
(E) Representative transmission electron micrographs of heparin-induced tau-HiBiT assemblies before and after sonication. Scale bar, 200 nm.
(F) Titration of tau-HiBiT assemblies complexed with recombinant LgBiT (0.2 μL/well) in vitro for 30 min; n = 4.
(G) Confocal microscopy images of HEK293T cells expressing NLS-EGFP-LgBiT (HEK-NGL), immunostained with anti-GFP and anti-LgBiT antibodies. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(H) Western blot of cytosolic and nuclear fractions of NGL lysates probing for LgBiT, GFP, the nuclear marker histone H3, and the cytosolic marker tubulin.
(I) Effect of trypsin protease (Try) treatment, which degrades extracellular luciferase, on the luminescent signal in NGL cells; n ≥ 3.
(J) Titration of tau-HiBiT assemblies on NGL cells for 1 h; n = 3.
(K) Time course of entry of 50 nM tau-HiBiT assemblies added to NGL cells; n = 3.
All error bars indicate mean ± SEM.