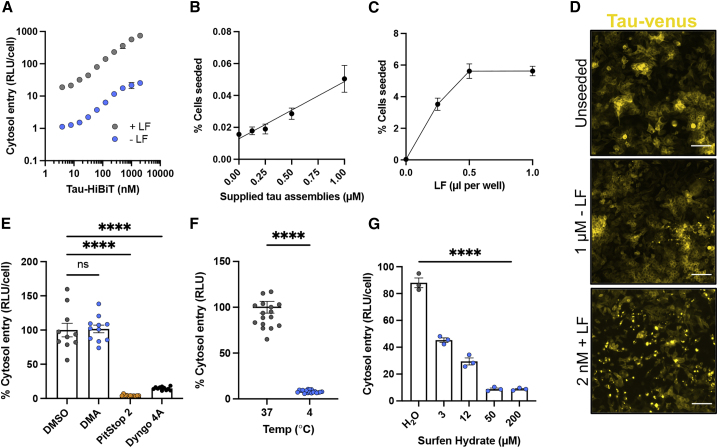
Figure 2.
Entry of tau assemblies into HEK293 cells relies on clathrin- and dynamin-dependent endocytosis
(A) Titrations of tau-HiBiT assemblies with or without Lipofectamine 2000 (LF) onto NGL cells. Entry was measured 24 h after challenge; n = 3.
(B) Percentage of P301S tau-venus cells seeded 72 h after challenge with the indicated concentration of tau assemblies; n = 3.
(C) Percentage of P301S tau-venus cells seeded 72 h after challenge with 2 nM tau assemblies supplemented with the indicated concentrations of LF; n = 3.
(D) Fluorescence microscopy images of unseeded control (PBS-treated) P301S tau-venus cells, cells challenged with 1 μM tau assemblies without LF, or cells challenged with 2 nM tau assemblies with LF. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(E) Effect of uptake inhibitors on entry of 50 nM of tau-HiBiT assemblies on HEK-NGL cells 1 h after challenge. HEK-NGL cells were pre-treated with DMA (200 μM), PitStop 2 (20 μM), Dyngo 4a (20 μM), or solvent (DMSO) for 30 min before challenge; n ≥ 3, N = 3 independent experiments.
(F) Effect of temperature on tau entry. 50 nM tau-HiBiT assemblies were supplied to HEK-NGL cells for 1 h at 37°C or 4°C; n = 16.
(G) The effect of surfen hydrate on tau entry to HEK-NGL cells in 1 h. Cells were pre-treated for 30 min with the indicated concentrations or equivalent dilutions of solvent (water) before 50 nM tau-HiBiT addition; n = 3.
All error bars indicate mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's comparisons (E and G) or Student's t test (F).