Figure 4.
YTHDF2 is required for early stages of the B cell immune responses but not for initial B cell activation
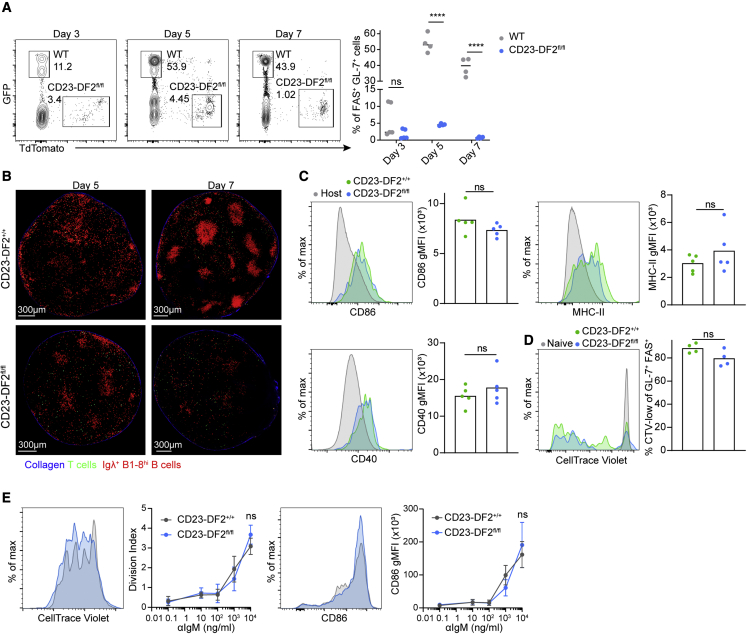
(A) WT GFP+ and TdTomato+ CD23-DF2fl/fl B1-8hi B cells were transferred to WT host mice at a 1:1 ratio. The frequencies of FAS+ GL-7+ cells were analyzed by flow cytometry 3, 5, and 7 days after NP-KLH immunization.
(B) CD23-DF2+/+ and CD23-DF2fl/fl B1-8hi TdTomato+ Igλ+ B cells and GFP+ CD4+ T cells were transferred separately to WT host mice. Lymph nodes were imaged by TPLSM 5 and 7 days after NP-KLH immunization. Images are representative of 3–4 independently analyzed lymph nodes.
(C) CD86, CD40, and MHC-II expression on transferred Igλ+ B1-8hi B cells were analyzed 16 h after immunization by flow cytometry. Data were pooled from five mice from two independent experiments.
(D) B1-8hi B cells were stained with CellTrace Violet prior to cell transfer and its dilution was measured 3 days after immunization by flow cytometry.
(E) Splenic cells derived from CD23-DF2+/+ and CD23-DF2fl/fl mice were stained with CTV and stimulated with 0.1–104 ng/mL αIgM for 3 days in vitro. Division index was calculated based on CTV dilution. CD86 expression was examined in similar manner. Plots are averaged from three independent experiments each performed with three replicates per condition. Dots represent mean ± SD.
Statistical significance was tested by one-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test (A), two-way ANOVA (E), or two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (C and D). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001; ns, not significant.