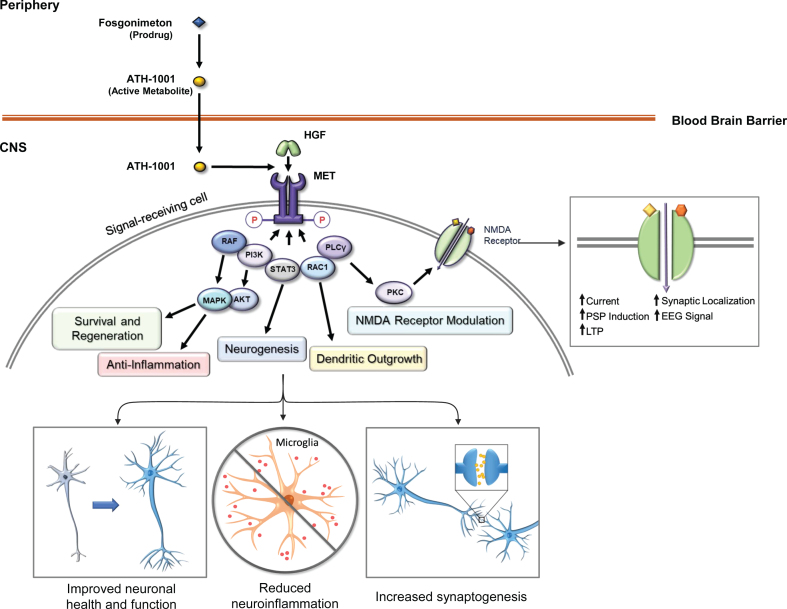
Fig. 1.
Fosgonimeton mechanism of action. The prodrug fosgonimeton is converted to the active metabolite ATH-1001. ATH-1001 enters the brain and enhances the HGF/MET neurotrophic system. HGF binding to MET induces phosphorylation of intracellular tyrosines on the MET receptor. MET activation results in changes in gene expression to stimulate various cell behaviors including regenerative and anti-inflammatory processes as well as neurotransmitter modulation. AKT, protein kinase B; EEG, electroencephalogram; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; LTP, long-term potentiation; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MET, MET receptor tyrosine kinase; NMDA, N-methyl D-aspartate; P, phosphorylated; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase C-gamma; PM, plasma membrane; PSP, post-synaptic potential; RAC1, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1; RAF, rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF) kinase; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.