Figure 1.
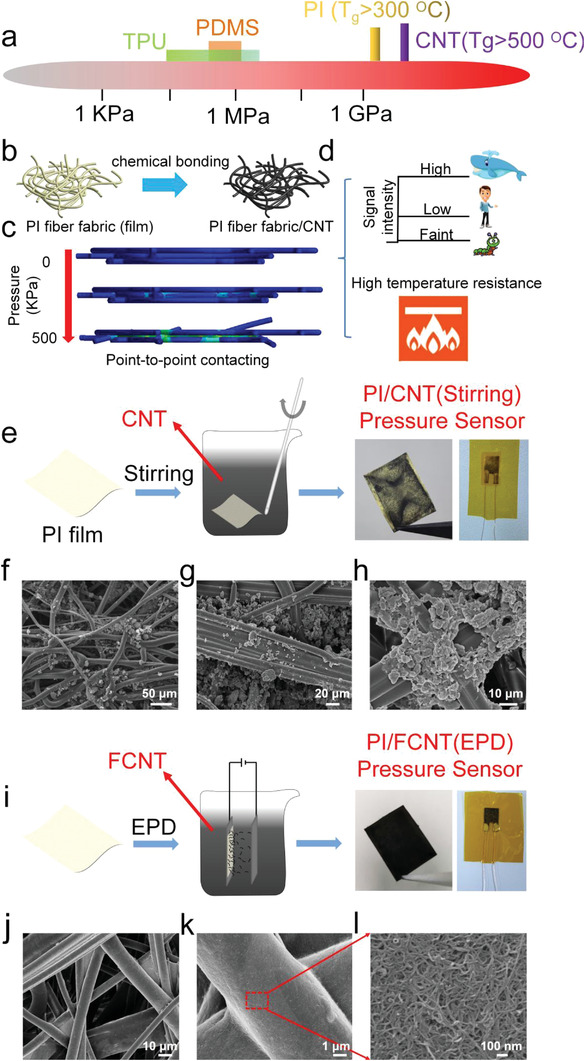
Materials selection, structure optimization, sensing mechanism, and the fabricated PI/CNT (stirring), PI/FCNT(EPD) pressure sensors. a) Materials selection: schematic illustration of Young's modulus of frequently used flexible matrix materials and conductive materials for the pressure sensors. (b) Structure optimization: PI fiber‐based fabrics and CNT is adopted as flexible matrix materials and conductive materials, respectively. c) Sensing mechanism: contacting points variation of the PI fiber fabrics/CNT under external pressure from 0 to 500 KPa. d) Schematic illustration of the response of the proposed PI fiber fabrics/CNT pressure sensor to faint, low, and high pressure, and such proposed pressure sensor possesses the merit of high‐temperature resistance. e) Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of PI/CNT (stirring) fabric, optical images of the PI/CNT(Stirring) fabric, and the final encapsulated PI/CNT(Stirring) pressure sensor. f–h) Top‐view SEM images of the PI/CNT(Stirring) fabric. i) Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of PI/FCNT(EPD) fabric, optical images of the PI/FCNT(EPD) fabric, and the final encapsulated PI/FCNT(EPD) pressure sensor. j–l) Top‐view SEM images of PI/FCNT(EPD) fabric.
