Figure 2. UPF1LL is enriched on NMD‐protected transcripts.
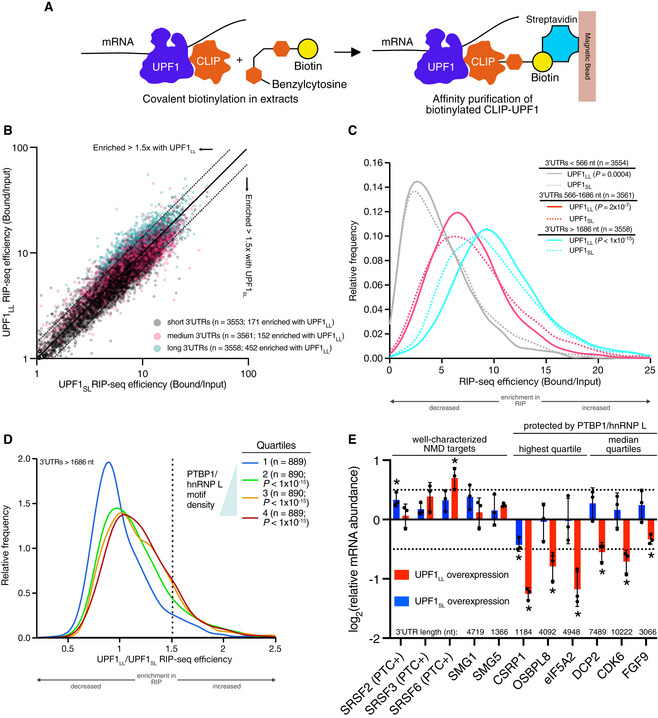
- Scheme for the CLIP‐UPF1 affinity purification (RIP) assay.
- Scatterplot of CLIP‐UPF1LL vs. CLIP‐UPF1SL RIP‐seq efficiency. mRNAs were binned according to 3’UTR length (short, medium, or long).
- Density plot of recovered mRNAs in CLIP‐UPF1LL or CLIP‐UPF1SL affinity purifications. mRNAs were binned according to 3’UTR length. Statistical significance was determined by K–S test.
- Density plot of recovered mRNAs in CLIP‐UPF1LL affinity purifications relative to that of CLIP‐UPF1SL. mRNAs were subdivided by PTBP1 and/or hnRNP L motif density within the 3’UTR, as indicated by the gradient triangle. Statistical significance was determined by K–W test, with Dunn’s correction for multiple comparisons.
- RT–qPCR analysis of indicated transcripts from CLIP‐UPF1 overexpression RNA‐seq experiments. Relative fold changes are in reference to the GFP‐expressing control line. Significance of CLIP‐UPF1SL or CLIP‐UPF1LL overexpression was compared to the GFP‐expressing control line. Asterisk (*) indicates P < 0.05, as determined by two‐way ANOVA. Black dots represent individual data points and error bars indicate mean±SD (n = 3 biological replicates). Dashed lines indicate log2 (fold change) of ± 0.5. For protected mRNAs, the motif density of PTBP1/hnRNP L within the 3'UTR is indicated. PTC+ indicates the use of primers specific to transcript isoforms with validated poison exons (Lareau et al, 2007; Ni et al, 2007). See also Dataset EV3 for P values associated with each statistical comparison.
Source data are available online for this figure.
