Figure 4.
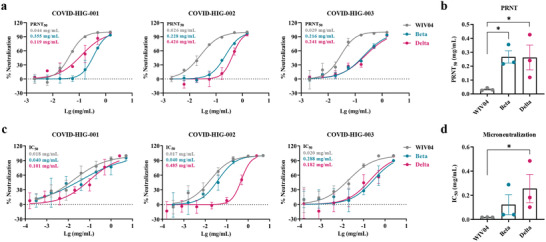
Neutralization of COVID‐HIG against SARS‐CoV‐2 WIV04, Beta, and Delta strains in vitro. a) PRNTs showed that COVID‐HIG‐001, ‐002, and ‐003 significantly inhibited infection by SARS‐CoV‐2 WIV04, Beta, and Delta strains in Vero E6 cells. Viruses were incubated with COVID‐HIG at 37 °C for 1 h. Next, Vero E6 cells were infected with WIV04, Beta, and Delta strains and stained with hematoxylin/eosin at 48 h (Beta and Delta variants) or 72 h (WIV04 strain) postinfection. The y‐axis represents percent inhibition. The mean from two independent replicates is shown (n = 2). b) Comparison of the PRNT50 of the variants and WIV04; statistical significance was analyzed using one‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05. c) Microneutralization assays showed that COVID‐HIG‐001, ‐002, and ‐003 significantly inhibited the SARS‐CoV‐2 WIV04, Beta, and Delta strains in Vero E6 cells. Viruses were incubated with COVID‐HIG at 37 °C for 1 h. Next, Vero E6 cells were infected with the WIV04, Beta, and Delta strains. After 24 h, the infected cell supernatant was analyzed using real‐time reverse transcription‐PCR (qRT‐PCR). The y‐axis represents percent inhibition. The mean from two independent replicates is shown (n = 2). d) Comparison of the IC50 of the variants and WIV04; statistical significance was analyzed using one‐way ANOVA. *P < 0.05. PRNT, plaque reduction neutralization tests.
