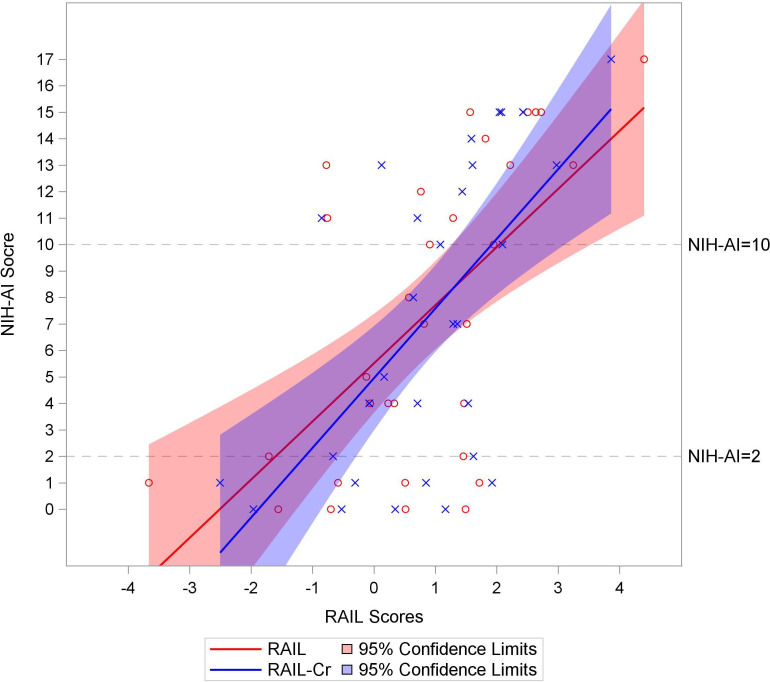
Figure 3.
Renal activity index for lupus (RAIL) and RAIL standardised for urine creatinine (RAIL-Cr) scores above two correlate with high activity lupus nephritis (LN). Distribution of the RAIL and RAIL-Cr score (x-axis) represented by red and blue liner regression lines and 95% confidence limits, respectively, against the available range of National Institute of Health-activity index (NIH-AI) scores (y-axis) in 32 patients with active LN. Each NIH-AI score by RAIL (red circle) and RAIL-Cr scores (blue cross) is marked in the figure. The relationship between NIH-AI and two RAIL scores are presented in liner regression lines with 95% confidence limits (RAIL in red line and RAIL-Cr in blue line). Grey dash lines (NIH-AI=2 and 10) are reference cut points for inactive, low-moderate and high LN activity.