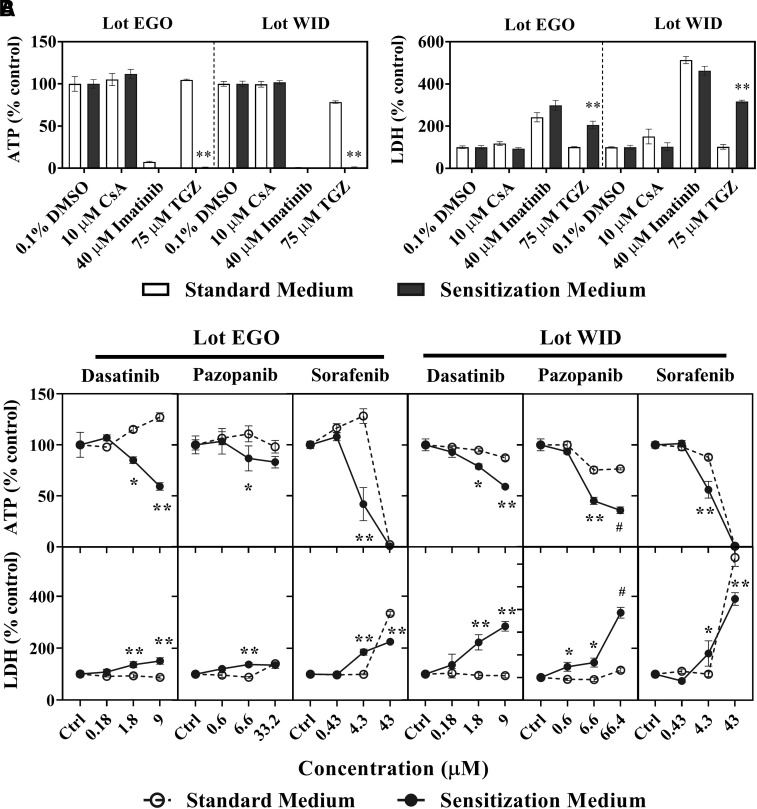
Fig. 1.
Bile acid-dependent toxicity from tyrosine kinase inhibitors in sandwich-cultured human hepatocytes (SCHH). Bile acid-dependent toxicity was measured in SCHH (lots EGO and WID) in Sensitization Medium (black bars, closed circles) and Standard Medium (white bars, open circles). SCHH were treated with (A) controls including 0.1% DMSO control, cyclosporine A (CsA; 10 μM), imatinib (40 μM) or troglitazone (TGZ; 75 μM) or (B) dasatinib, pazopanib, or sorafenib for 24 hours. ATP content and LDH release were normalized to 0.1% DMSO control. Data are shown as mean and standard deviation (n = 3). Statistically significant differences were determined by a repeated measures two-way ANOVA, with multiple comparisons corrected using the Sidak test (* P value < 0.05, **<0.0001, standard versus sensitization medium). #Precipitation was observed at 66.4 μM pazopanib, and therefore, the highest concentration was decreased to 33.2 μM for lot EGO. Imatinib and TGZ ATP values <2% of control are not visible in Fig. 1A.