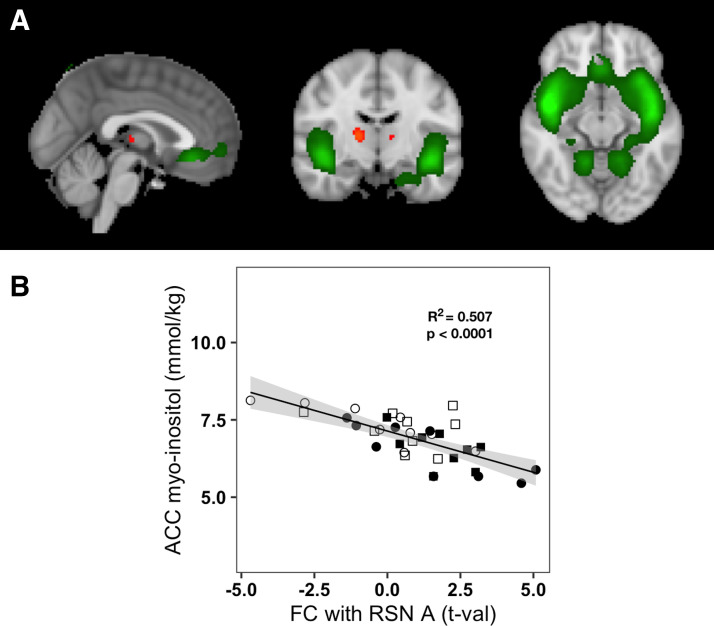
Figure 4.
Relation of pregenual anterior cingulate cortex (pgACC) myoinositol to functional connectivity of the salience network (RSN A) with thalamus. A: RSN A, common to all participants and conditions, is overlaid in green on the standard MNI-152 brain; regions overlaid in red-yellow scale show the thalamic region where increased functional connectivity with RSN A was associated with lower pgACC myoinositol (MI) concentrations. Images are shown using the radiological convention: left—sagittal (x = 0 cm); middle—coronal (y = −11.6 cm); right—axial (z = −11.4 cm). B: plot of pgACC MI concentrations vs. functional connectivity of RSN A with thalamus for all participants and conditions. Empty shapes indicate the basal euglycemia conditions of visits 1 and 2: empty circle = visit 1, empty square = visit 2; filled shapes indicate the clamps; filled circles indicate the hyperglycemic clamp; filled squares indicate the euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp. The solid black line represents the linear fit of pgACC MI concentrations to functional connectivity with RSN A (Pearson R2 = 0.507, P < 0.0001) and the gray area represents the 95% confidence interval.