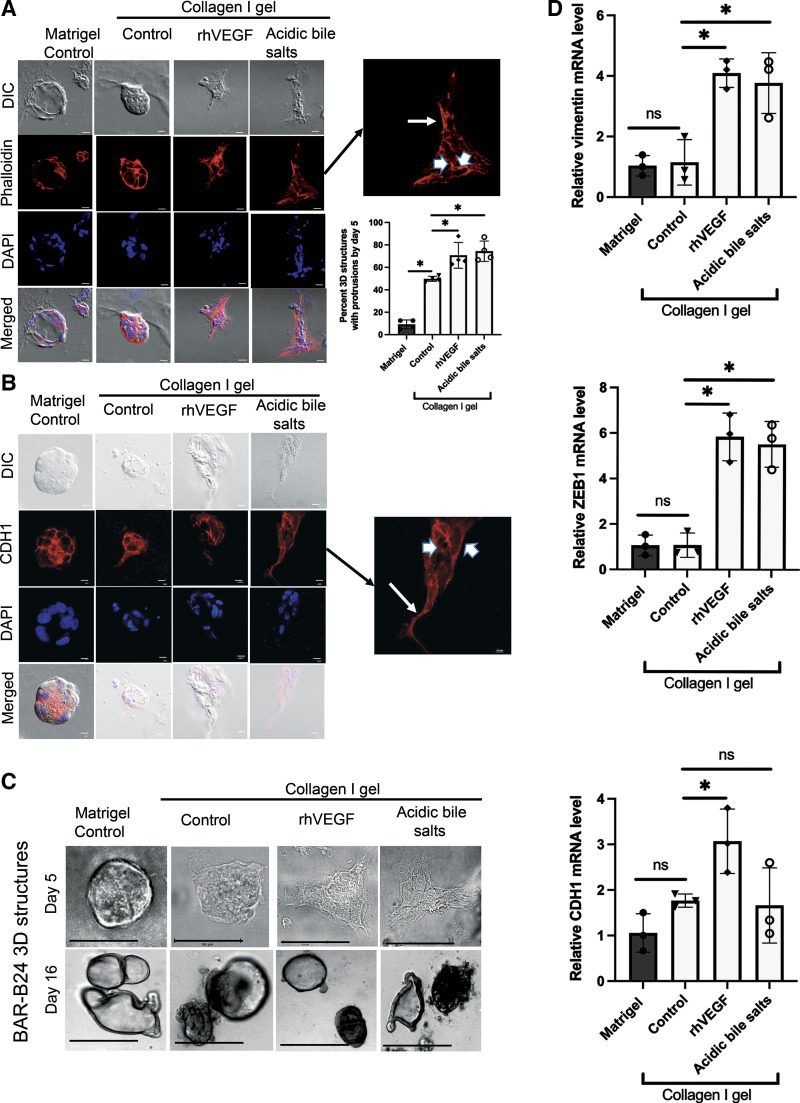
Figure 6.
Acidic bile salt treatment of early stage, three-dimensional structures of Barrett’s epithelial cells increase cell spreading via formation of finger-like protrusions associated with reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cytoplasmic relocalization of CDH1, and increased expression of mesenchymal markers. Representative DIC and fluorescence microscopy images of phalloidin (A) or CDH1 staining (B) in day 5. BAR-B24 3-D structures embedded in Matrigel and collagen I. Note that acidic bile salt treatment significantly increased the percentage of 3-D structures with protrusions compared with collagen I control cells. Scale bar = 275 µm. Magnified insets demonstrate cytoplasmic staining for phalloidin and CDH1 in cells at the leading edge of the protrusions (arrows), and membranous staining for these proteins that encircle the cell perimeter in cells at the nonprotrusive base (arrowheads). DAPI was used as a nuclear counterstain. C: representative phase contrast morphological images in day 5 and day 16. BAR-B24 3-D structures embedded in Matrigel and collagen I. Note that treatment with acidic bile salts caused protrusions in the day 5 structures but not in the day 16 structures. Scale bar = 50 µm for day 5; Scale bar = 275 µm for day 16. D: representative qPCRs for vimentin, ZEB1, and CDH1 mRNA levels in day 5 BAR-B24. 3-D structures embedded in Matrigel or collagen I with or without acidic bile salts. In all panels, rhVEGF served as a positive control. Bar graphs depict the means±SD from ≥ 3 technical replicates. *P≤ 0.05; ns, nonsignificant; one-way ANOVA. All experiments in BAR-B24 were repeated three times. CDH1, E-cadherin; DAPI, 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DIC, differential interference contrast; qPCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; rhVEGF, recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor; ZEB, zinc finger transcription factor.