Figure 3. An Increase in Actomyosin Duty Cycle by Mutant Cardiac Myosin Leads to Prolonged Muscle Contraction in HCM.
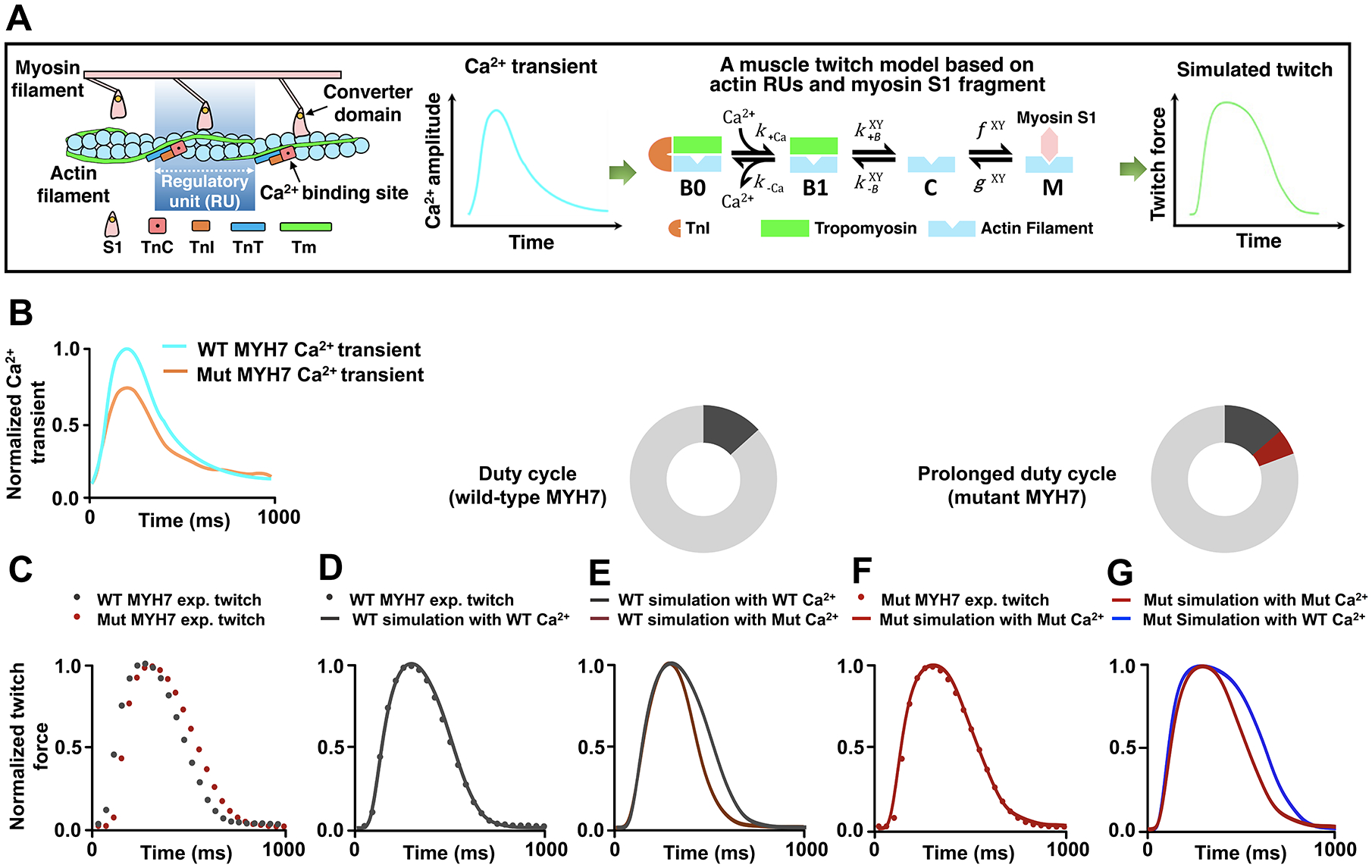
A, Schematic illustration of a computational model for muscle contraction based on cooperative myofilament activation27, 28, 37. Left panel: The model depicts the function of individual thin filament regulatory units (RUs), consisting of 7 actin monomers, TnC, TnI, and tropomyosin (Tm), in conjunction with the S1 fragment of myosin head. Right panel: The model takes a calcium transient as input and outputs activation of the myofilament dependent on the model parameters which describe myofilament protein interactions. Each RU exists in one of four states illustrating Ca2+ binding (from Ca2+-free B0 to Ca2+-bound B1 blocked states), Tm shifting (from B1 blocked to the closed [C] states), and myosin attachment (from the closed [C] to open [M] states). Note that the transition between closed and open (M) states is determined by the simplified crossbridge attachment (f) and detachment (g) rates27, 28, 37. The B↔C and C↔M transition rates are functions of Tm states of the two nearest neighboring RUs (X and Y). Also see additional information in the Expanded Methods in the SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. B, Experimental Ca2+ transients collected from both the wild-type (WT) and MYH7 mutant (Mut) iPSC-CMs. Ca2+ transients (Figure S4A–4C) were normalized and scaled to reflect relative average properties from the summary data, with the WT Ca2+ transient normalized at a diastolic value of 0.1 μM and a maximum value of 1.0 μM. C, Experimental twitches collected from both the WT and the MYH7 Mut EHTs and normalized to their individual maximum force for model analysis. D, The WT twitch was simulated by inputting the realistic WT Ca2+ transient into the model and optimizing the parameter set through minimization of the root mean square error using the particle swarm stochastic optimization algorithm. See details in the Expanded Methods. E, The MYH7 Mut Ca2+ transient was input into the model while keeping the parameters that fit the WT twitch. F, MYH7 Mut twitch was simulated using the MYH7 Mut Ca2+ transient and increasing the myosin duty cycle (δ) by 30% from the WT fit parameters (δWT 0.20; δMut 0.26). No other parameters were changed from the WT fit except for the myosin attachment rate f. See Table S2 for myofilament model parameter sets. G, The WT Ca2+ transient was input into the model with the mutant parameter set, representing only an increase in the myosin attachment rate.
