Fig. 3. Populations code with increasing levels of abstraction across cortical areas.
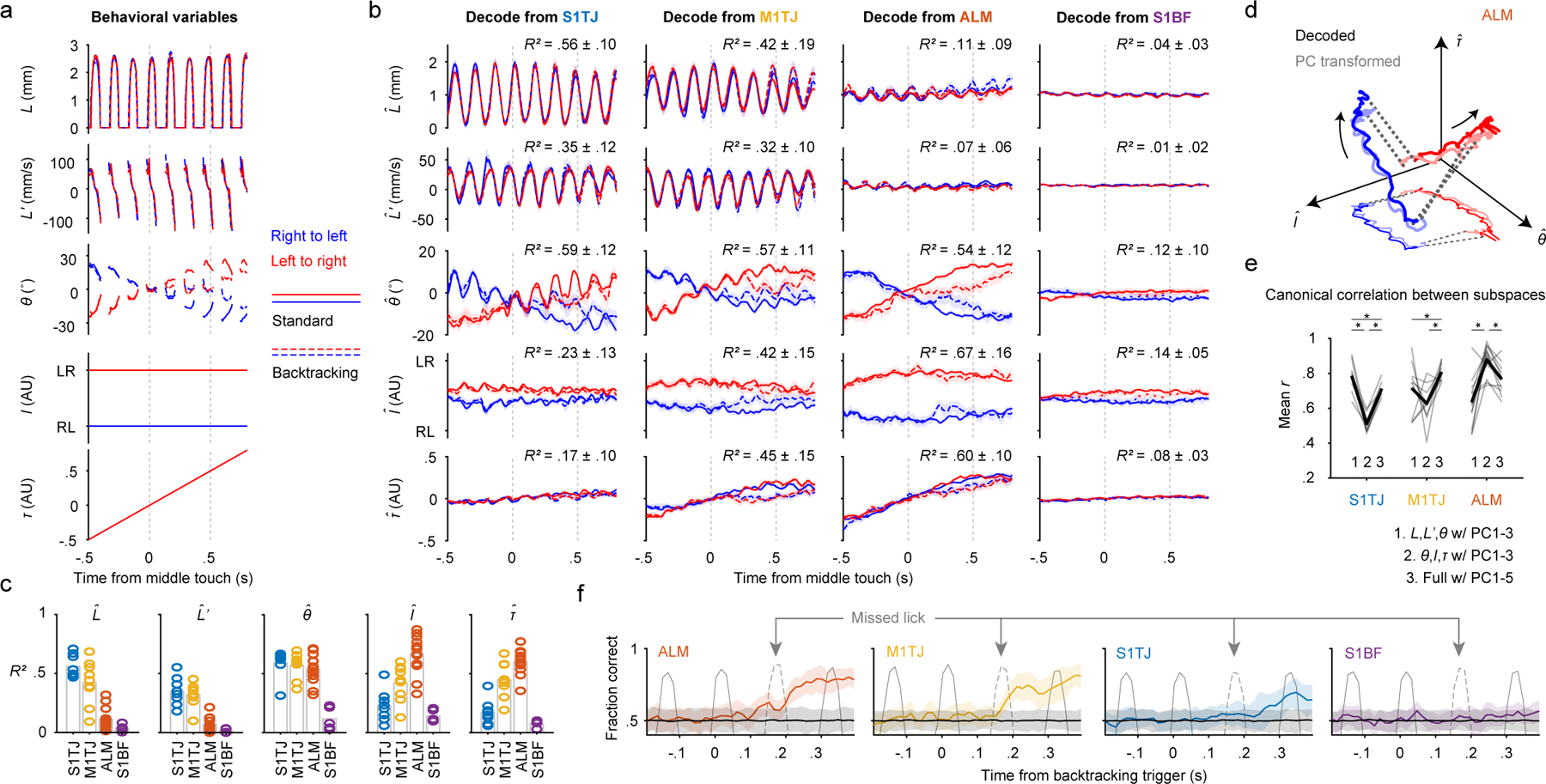
a, Time series of the behavioral variables (mean ± 99% bootstrap confidence interval; n = 2684 trials) for different sequence types. Time points where >80% of trials had no observations are not plotted.
b, Decoding of the five behavioral variables (rows) from populations recorded in S1TJ, M1TJ, ALM, and S1BF (columns). Crossvalidated R2 for each region and variable is given (mean ± SD). S1TJ, n = 8 sessions; M1TJ, n = 9 sessions; ALM, n = 13 sessions; S1BF, n = 5 sessions for all Fig. 3 panels unless otherwise noted. Same plotting conventions as in (a).
c, Bars show means of R2 values from (b). Circles show R2 for individual sessions.
d, Neural trajectories from ALM (mean) during standard sequences (linked by dashed lines). Arrows indicate direction of time. Decoded trajectories (darker thick curves) are overlaid with trajectories (lighter thick curves) in the space of the top 3 PCs, after a linear transformation. A projection into the I-θ plane is depicted with thinner and lighter curves.
e, Mean canonical correlation coefficients (r) for each neural population (gray traces) across three conditions. Average mean r values for each condition are shown in black. ∗ p < 0.001, not significant p > 0.05 otherwise, paired two-tailed permutation test.
f, Classification of standard vs backtracking sequences from population activity. Accuracy is the fraction of trials correctly classified (mean ± 95% hierarchical bootstrap confidence interval; ALM, n = 6 sessions). Colored traces and error shadings are from original data, black traces and shadings from data with randomly shuffled trial labels. Average time series of tongue length are overlaid (gray traces) to show the concurrent behavior. The dashed gray traces indicate licks that unexpectedly missed the port as a result of the port backtracking.
