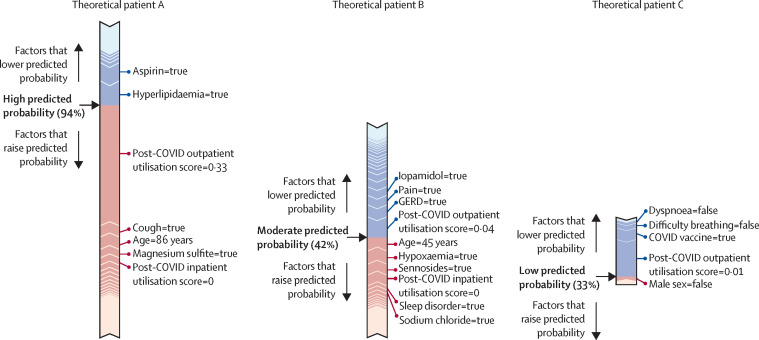
Figure 5.
Example paths taken by the machine learning models to classify patients with potential long COVID
Force plots showing the contribution of individual features to the final predicted probability of long COVID, as generated for individual patients by the all-patients model (A), hospitalised model (B), and non-hospitalised model (C). Features in red increase the predicted probability of long COVID classification by the model, whereas features in blue decrease that probability. The length of the bar for a given feature is proportional to the effect that feature has on the prediction for that patient. The final predicted probability is shown in bold. GERD=gastroesophageal reflux disease.