Fig. 2.
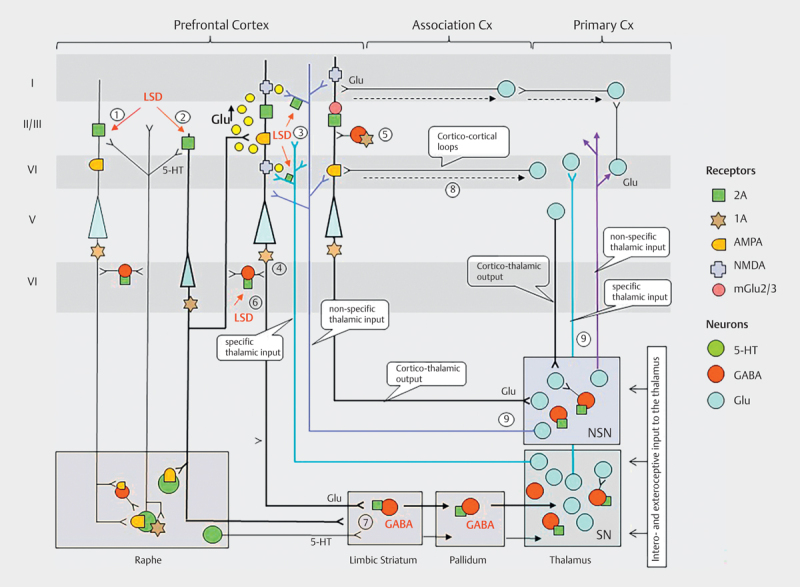
Working hypothesis of psychedelic drug effects on cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical and cortico-cortical circuits of information flow: The schema in Fig. 2 comprises central brain networks on the effects of psychedelic drugs responsible for bottom-up sensory input via the thalamus to the cortex and top-down cortico-striato-thalamic, cortico-thalamic and/or cortico-cortical control of information processing. The model is based mostly on data obtained on the action of LSD and DOI in animals as well as from some studies with LSD and psilocybin in humans. The 5-HT2A receptors are highly expressed in the apical dendrites of layer 5 pyramidal (L5p) neurons in the cortex and are particularly enriched in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) 129 130 131 . A smaller proportion is located pre-synaptically on thalamocortical afferents projecting to the neocortex 96 . 5-HT2ARs are also expressed on GABAergic interneurons in the cortex and subcortical structures 131 . LSD and DOI both increase extracellular glutamate levels via activation of post-synaptic 5-HT2A receptors on deep layers 5 and 6 pyramidal neurons (L5p) (stage 1) and on Lp6 (stage 2) neurons projecting to L5p neurons 96 132 133 as well as via activation of pre-synaptic 5-HT2A receptors on specific (SP) and non-specific (NSP) thalamocortical afferents 96 134 . Psychedelics such as LSD can also stimulate 5-HT1A receptors on the hillock on Lp5 and Lp6 neurons (stage 4) and cortical GABAergic interneurons (stage 5) resulting in both inhibition and disinhibition of prefrontal pyramidal cell activity 132 135 136 . Furthermore, LSD or DOI are also potent partial agonists at cortical (stage 6) and subcortical (striatal, pallidal or thalamic) (stage 7) 5-HT2A receptors in GABAergic interneurons 137 138 . Despite this partially inhibitory mechanisms, this LSD- or DOI-induced increased glutamate release produces a striking net-excitatory effect on L5p neurons 139 140 141 and promotes synaptic plasticity via AMPA and NMDA receptor-dependent mechanisms 98 105 106 133 142 . L5P neurons affect both thalamic and cortical processing and have the unique ability to couple thalamo-cortical (stage 8) and cortico-cortical loops (stage 9) of information streams with each other 143 . This is thought to provide a mechanism through which the state and content of consciousness are functionally coupled 134 . Psychedelics appear to affect this extended thalamic-cortical broadcasting system and thus consciousness as a whole, by simultaneously producing sensory flooding and arousal via reduced thalamic gating of interoceptive and exteroceptive stimuli and by altering the meaning and attachment of percepts due to disrupted cortico-cortical interactions 19 109 . In this model, thalamic gating is thought to be under the control of glutamatergic cortico-striatothalamic and cortico-thalamic loops projecting back to the cortex, in addition to being under the modulatory influence of serotonergic (and dopaminergic) projections from the raphe (and the VTA) to several parts of the CSTC.
