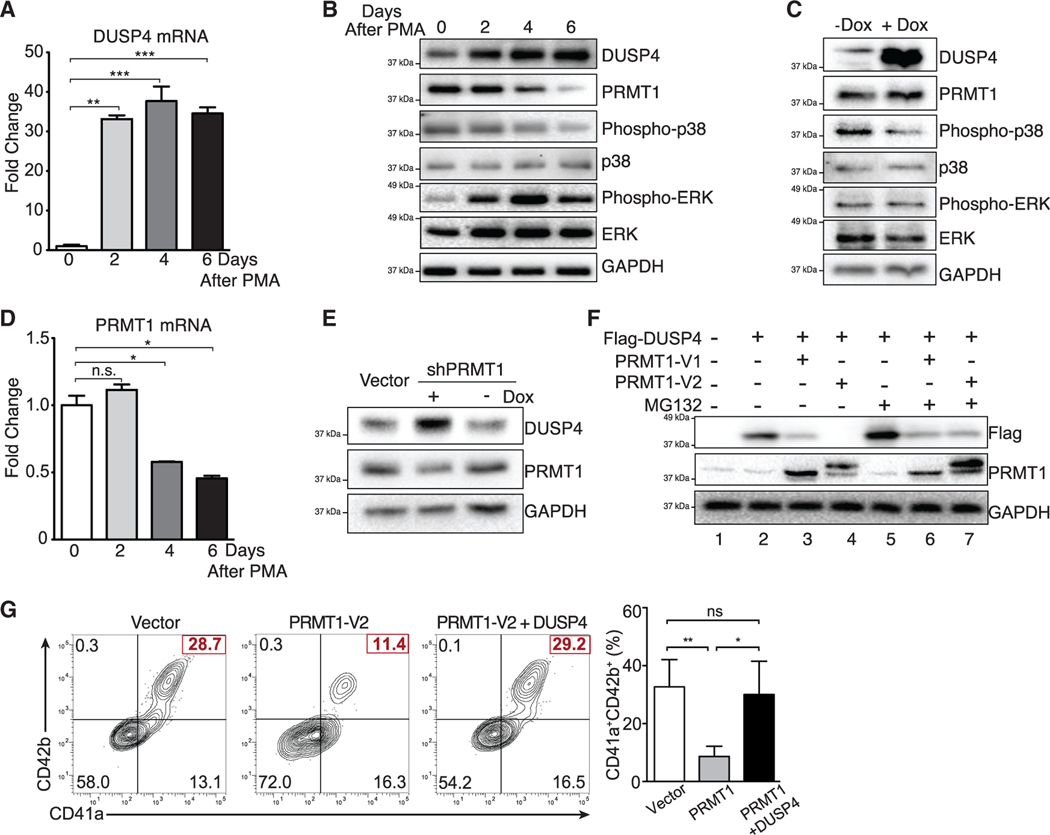
Figure 3. Crosstalk between DUSP4 and PRMT1 for MAPK signaling in Mk differentiation.
(A) DUSP4 mRNA level in PMA-treated MEG-01 cells. Cells were harvested at indicated time intervals, and the extracted mRNAs were quantified by real-time PCR. Representative statistics are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired t test, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001 (n = 3, independent experiments).
(B) MAPK-related proteins and PRMT1 in MEG-01 cells after PMA stimulation. Protein extracts were collected at indicated time intervals for western blotting.
(C) Regulation of MAPK signaling upon DUSP4 overexpression. MEG-01 cells were treated overnight with doxycycline to induce DUSP4 ectopically expressed from lentivirus. Cell extracts were collected for western blotting (n = 3, representative western blots).
(D) PRMT1 mRNA level in MEG-01 cells during the course of PMA-stimulated Mk differentiation. Representative statistics were shown as mean ± SD, two-tailed unpaired t test, *p ≤ 0.05 (n = 3, independent experiments).
(E and F) PRMT1-dependent regulation of DUSP4 protein. NB4 cells that conditionally express shRNA against PRMT1 were treated with doxycycline to induce PRMT1 knockdown (E). DUSP4- and PRMT1-encoding plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells for their overexpression in the presence or absence of MG132 treatment (F).
(G) Antagonistic roles of PRMT1 and DUSP4 on Mk differentiation of human CD34+ cells. Human CD34+ cells were infected with PRMT1 lentivirus (puromycin-R) and DUSP4 lentivirus (GFP), followed by puromycin selection and Mk differentiation. Representative plots and statistics are shown (n = 3, independent experiments). Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed paired t test, *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.