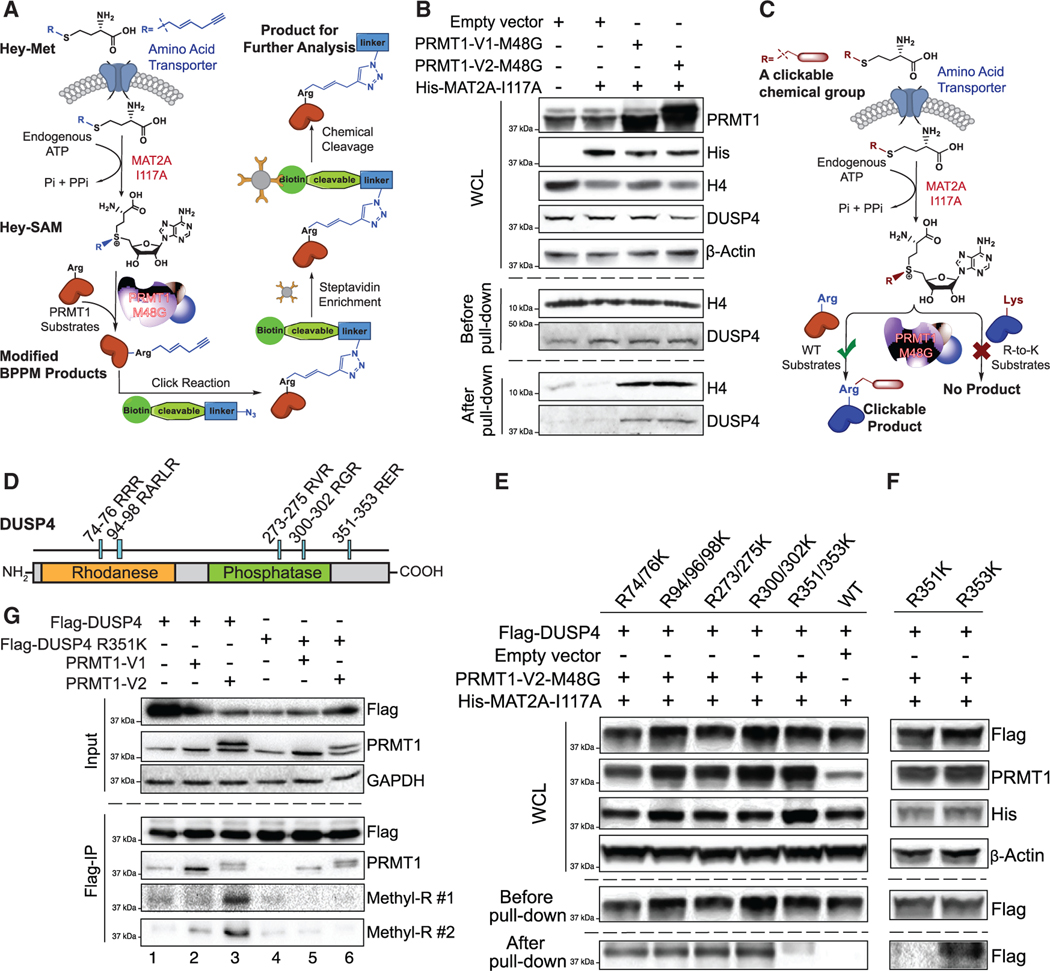
Figure 5. R351 methylation of DUSP4 by PRMT1.
(A) Schematic of the next-generation live-cell BPPM technology to uncover substrates of PRMT1.
(B) Immunoblotting readouts of H4 and DUSP4 as PRMT1 targets enriched via the BPPM technology using HEK293T cells (n = 3, representative western blots).
(C) Schematic description of the next-generation live-cell BPPM technology to reveal methylation sites of PRMT1. Candidates of methylated arginine (Arg) residues on a protein substrate are mutated to lysine (Lys). The resulting arginine-to-lysine mutation is expected to diminish or abolish the BPPM-associated labeling.
(D) DUSP4 sequence with functional domains and RXR motifs highlighted.
(E and F) Revealing PRMT1 methylation sites on DUSP4 with the next-generation live-cell BPPM technology. The DUSP4 variants contain dual arginine-to-lysine mutations at RXR motifs (E) and the point mutations at R351 and R353 (F), respectively (n = 3, representative western blots).
(G) Validating PRMT1-invovled R351 methylation on DUSP4 with anti-methylarginine antibodies in HEK293T cells (n = 3, representative western blots). Two anti-methyl-arginine antibodies were used to determine the presence of arginine methylation in DUSP4.