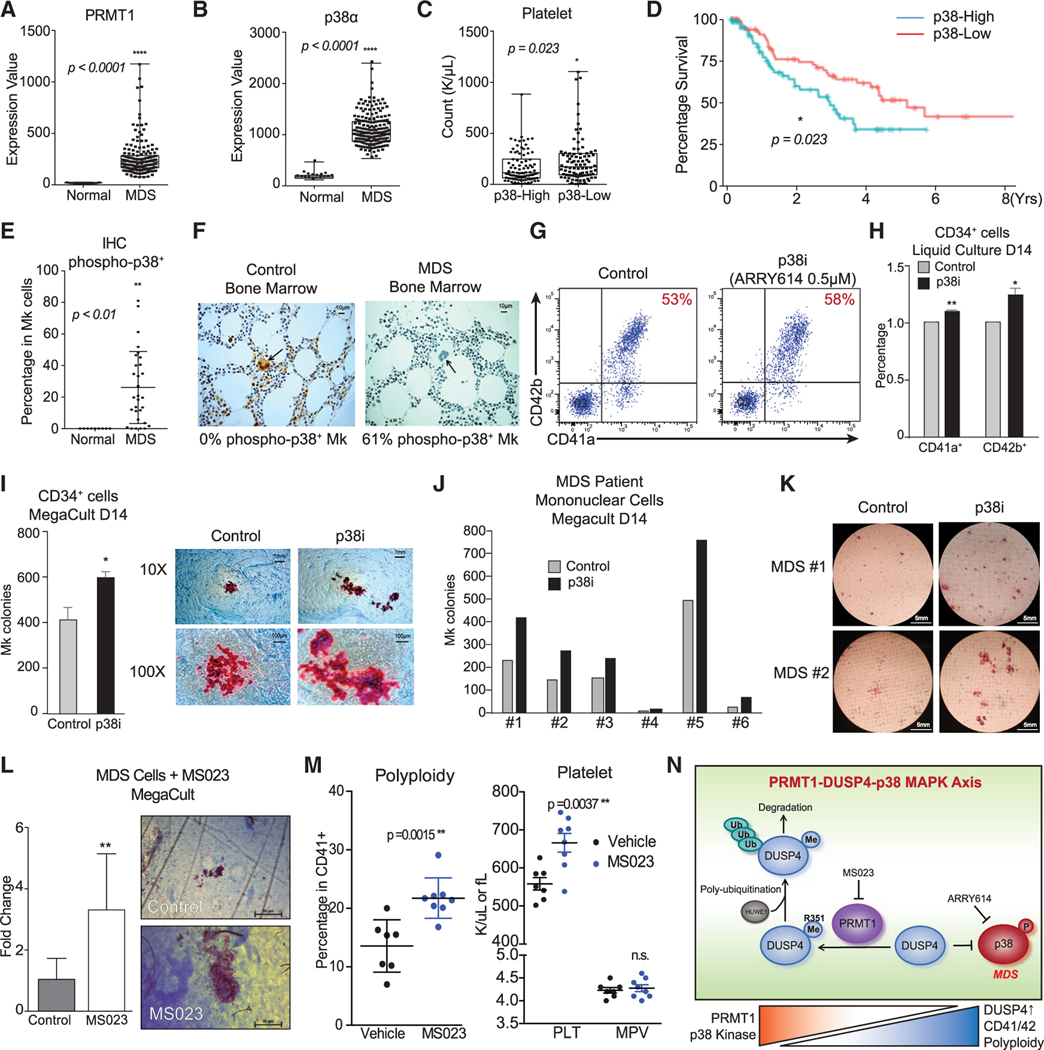
Figure 7. Clinical implication and pharmacological targeting of the p38-DUSP4-PRMT1 axis in MDS.
(A and B) Gene expression of PRMT1 and p38α in MDS patients and healthy donors with array-based analysis. The CD34+ HSPCs of MDS patients (N = 183) and age-matched healthy controls (N = 17) were analyzed for PRMT1 expression (A) and p38α expression (B). Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired t test, ****p ≤ 0.0001.
(C) MDS cohorts as classified by low and high expression of p38α MAPK on the basis of median expression levels. The subjects with high p38α expression showed significantly lower platelet counts. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired t test, *p ≤ 0.05.
(D) Survival curves of MDS patients classified by low and high expression of p38α MAPK. The MDS patients with higher p38α expression in HSPCs showed significantly worse overall survival. *p ≤ 0.05.
(E and F) Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis for phosphorylation-activated p38α MAPK of age-matched healthy controls and MDS BM samples from a clinical trial with the p38α inhibitor pexmetinib (ARRY614, labeled as p38i). MDS BMs showed significantly higher phospho-p38α staining in megakaryocytes (E). Representative stains are shown (F). Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed unpaired t test, **p ≤ 0.01.
(G–I) Effects of the p38α inhibitor pexmetinib (labeled as p38i) on normal CD34+ cells. Normal CD34+ cells were grown in liquid culture conditions in the presence and absence of pexmetinib and analyzed for CD41 and CD42 expression by representative charts shown (G) and averaged FACS data (H) (n = 2, independent experiments). (I) Normal CD34+ cells were also grown for MegaCult assay for production of megakaryocyte colonies (n = 2, independent experiments). Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed paired t test, **p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.
(J and K) Analysis of BM mononuclear cells (MNCs) of MDS patients with MegaCult assay for production of megakaryocyte colonies in the presence or absence of the p38α inhibitor pexmetinib (or p38i). Six MNC samples were examined (J) with the representative images shown (K).
(L) Analysis of MNCs of MDS patients (n = 6) with MegaCult assay for production of megakaryocyte colonies in the presence or absence of a PRMT1 inhibitor MS023. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Two-tailed paired t test, **p ≤ 0.01.
(M) Mk polyploidy and platelet count analysis in C57BL6/J mice treated with MS023. BM CD41+ cells were analyzed by FACS for polyploidy. The number of platelets in peripheral blood and MPV (mean platelet volume) were analyzed by a Hemavet machine.
(N) Mechanistic description of Mk differentiation via the PRMT1-DUSP4-p38 axis. Mk progenitors undergo abnormal differentiation in MDS by upregulation of PRMT1, which leads to p38 kinase activation. The relative levels of phospho-p38 are regulated by DUSP4. DUSP4 R351 is subject to PRMT1-medidated methylation, which leads to polyubiquitylation by HUWE1 and then degradation. Collectively, the PRMT1-DUSP4-p38 axis determines generation of Mk progenitor cells and the maturation of Mk cells.