Figure 5.
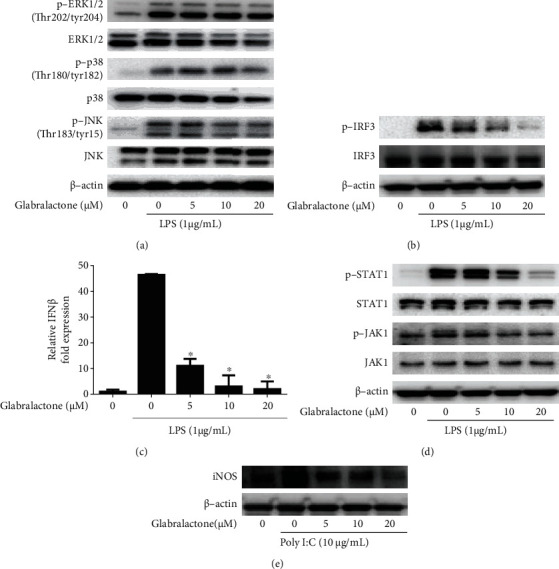
Effect of glabralactone on the TRIF-dependent TLR signaling pathway. (a) Effect of glabralactone on the protein expression of MAPK signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were pretreated with glabralactone for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for an additional 30 min. Proteins were analyzed by Western blotting. (b) Effect of glabralactone on the protein expression of IRF3 in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were pretreated with glabralactone for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 3 h. After incubation, total proteins were extracted, and IRF3 and p-IRF3 protein expressions were analyzed by Western blotting. (c) Effect of glabralactone on the mRNA expression of IFN-β in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were pretreated with glabralactone for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 4 h. The mRNA expression of IFN-β was analyzed by using reverse transcription and real-time PCR. ∗p < 0.05. (d) Effect of glabralactone on the JAK/STAT pathway protein expression in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Cells were pretreated with glabralactone for 30 min and then stimulated with LPS (1 μg/mL) for 3 h. After incubation, total proteins were extracted, and protein level was analyzed by Western blotting. (e) Effect of glabralactone on poly (I:C)-induced iNOS expression. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with glabralactone for 30 min and then stimulated with poly I:C (10 μg/mL) for 12 h. After incubation, total proteins were extracted, and iNOS protein level was analyzed by Western blotting. β-Actin was used as an internal standard. Glabralactone was dissolved in 100% DMSO, and the final concentration of DMSO was adjusted to 0.1%.
