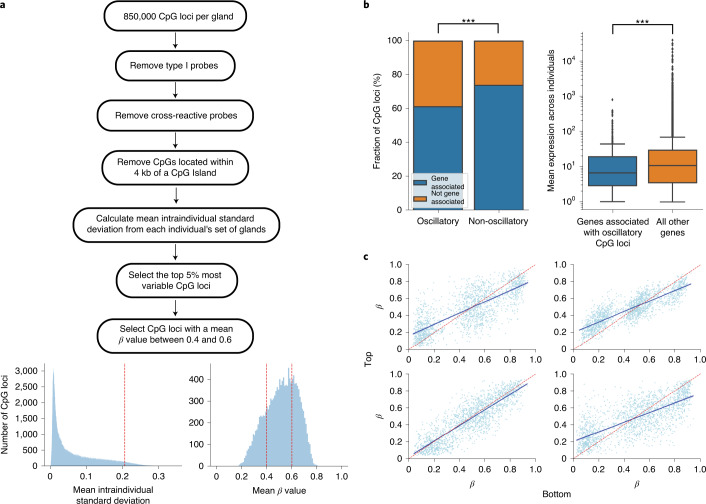
Fig. 2. Identification of selectively neutral fCpG loci.
a, Workflow used to identify fCpG loci that exhibit high intraindividual heterogeneity. Input data were the ~850,000 CpG loci assayed by an Illumina EPIC array. We removed type I probes and probes that cross-hybridize highly homologous DNA regions. For each CpG locus, we calculated the standard deviation for each set of approximately four crypts per individual and then calculated the mean standard deviation across the cohort as a metric for the intraindividual heterogeneity. We selected the top 5% most highly variable CpG loci and then removed CpG loci that have a mean β value (across the entire cohort) less than 0.4 or greater than 0.6; kb, kilobases. b, Left: fCpGs are enriched for CpG loci not associated with any genes (P = 6.5 × 10−34, chi-squared test). Right: the set of genes associated with fCpG loci exhibit lower average RNA expression (P = 6.6 × 10−6, two-sided Welch’s t-test performed following the log-transformed data) in normal colon than those genes associated with non-fCpG loci (center line, median; box limits, upper and lower quartiles; whiskers, 1.5 interquartile range). ***P < 0.001. c, β values of fCpG loci are correlated between the bottom and top halves of a crypt.