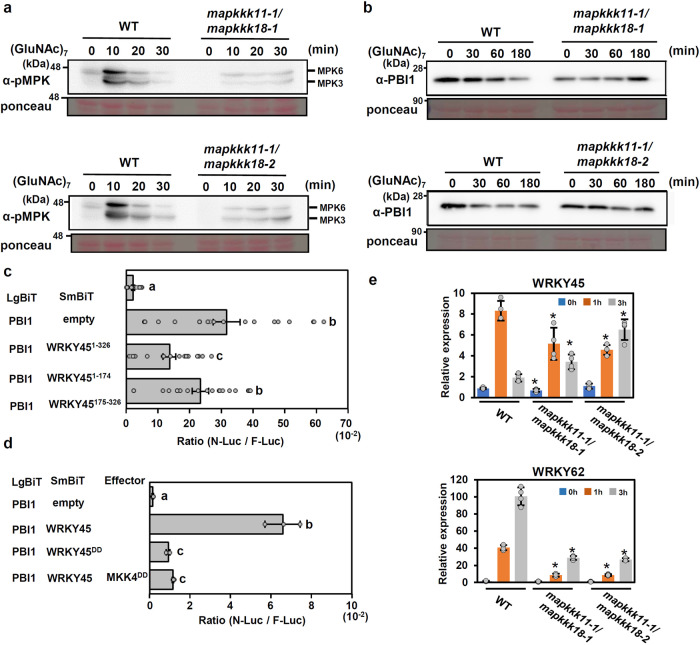
Fig. 6. MAPKs regulate PBI1 degradation.
a Chitin-induced MAPK activation in two mapkkk11/mapkkk18 mutants. Total proteins were prepared from rice suspension-cultured cells after treatment with 2 μg/ml (GluNAc)7 and subjected to immunoblots with α-pMAPK. b Chitin-induced PBI1 degradation was inhibited in the mapkkk11/mapkkk18 mutants. Total proteins were prepared as for (a) and probed with α-PBI1. c The interactions between PBI1 and full length WRKY45 or WRKY45 fragments were analyzed using split NanoLuc luciferase assays. PBI1 was fused to LgBiT, and the WRKY45 fragments were fused to SmBiT. F-Luc was used as an internal control. Rice protoplasts were transfected with the constructs and the interactions were indicated by the N-Luc to F-Luc ratios. Data are means ± SE. n = 19 biologically independent replicates. Different letters above the data points indicate significant differences (p < 0.01, two-sided Welch’s t test). d Phosphor-mimic mutation of WRKY45 reduces the interaction with PBI1. Split NanoLuc luciferase assays were carried out by transient expression of PBI1-LgBiT and WRKY45-SmBiT or WRKY45DD-SmBiT with or without MKK4DD in rice protoplasts. Values are means ± SE. n = 3 biologically independent replicates. Different letters above the data points indicate significant differences (p < 0.01, two-sided Welch’s t test). e The expression levels of WRKY45 and WRKY62 in mapkkk11/mapkkk18 suspension-cultured cells treated with 2 μg/ml (GluNAc)7 were analyzed using quantitative real-time PCR. Data are means ± SD. n = 4 biologically independent replicates. The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences from the WT controls by two-sided Student’s t-test (P < 0.05). All above experiments were repeated three times with similar results.