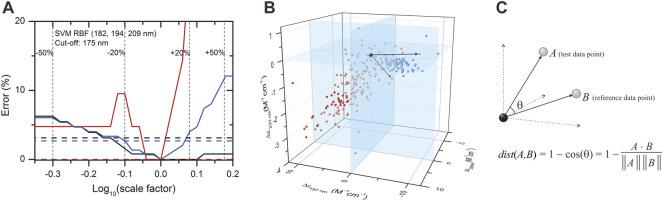
FIGURE 3.
Effect of concentration error on disordered–ordered classification and introduction of the KNN-cosine method. (A) Error of the SVM–RBF algorithm as a function of the scaling factor on the spectra of the database with 175 nm cutoff are shown for disordered (red) and ordered (black) structures. The global error is shown in blue. Dashed lines show the errors of classification using the KNN-cosine algorithm for disordered (red), ordered (black), and the overall error (blue). For convenience, ±20% and ±50% changes in the concentration (i.e., in the scaling factor) are shown. (B) Reference points in the space determined by the CD data measured at 197, 206, and 233 nm wavelengths and an example for vectors by using the KNN-cosine method. Red and blue points represent ordered and disordered proteins, respectively. (C) The distance metric of this KNN algorithm uses the cosine of the angle between vectors pointing from the origin to data points. The prediction is based on the labels (ordered/disordered) of the first 10 reference points with the lowest “distance” from the test point. The direction and the angles of the vectors will not change with scaling, that is, the method is independent of concentration errors.