FIGURE 2.
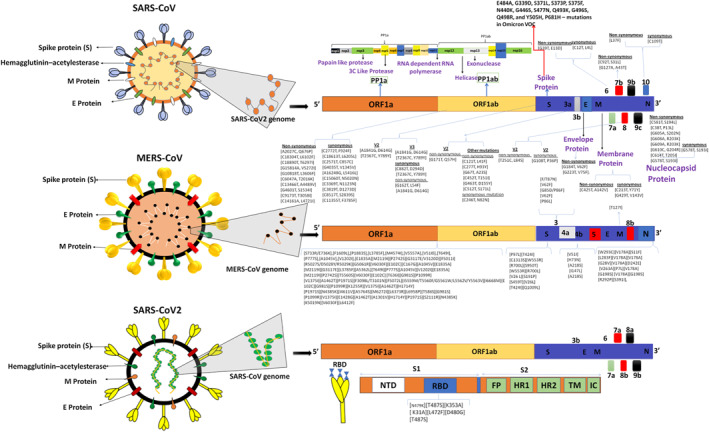
Phylogenetic and mutational analyses of lethal (or associated with the disease severity) coronavirus mutations in the reference genome. Upper panel – SARS‐CoV‐2: Approximately 4000 mutations were observed in S‐protein of SARS‐CoV‐2. Majority of these mutations do not influence COVID‐19 disease severity. Synonymous & nonsynonymous SARS‐CoV‐2 mutations in ORF1ab, S‐protein (v2, v3), E/M/N proteins, and amino acid substitutions (E484K) can enhance virus transmissibility via more effective S‐protein and ACE2 receptor binding. 81 Middle panel: MERS CoV: The Saudi Arabian human isolates contained a number of unique amino acid substitutions in ORF1ab (41 mutations), N‐protein (10 mutations mutations), S‐protein (9), and ORF4b (5 mutations) which could enhance virulence of this strain in human body. Lower panel: SARS‐CoV: Naturally selected mutations were observed in RBD region (7 mutations). These mutations can modulate RBD/hACE2 interactions of evolving SARS‐CoV variants
