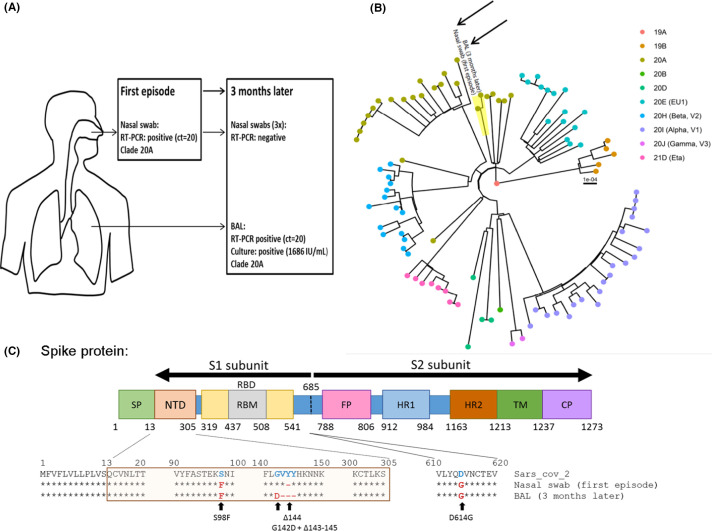
FIGURE 1.
SARS-CoV-2 compartmentalization in a kidney transplant recipient (KTR) with negative nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR after rituximab. (A) Summary of SARS-CoV-2 virological results from the first and second COVID-19 infections including RT-PCR results in a nasal swab and BAL, infectious titer and clade according to Nextclade classification. (B) Phylogenetic tree from the first (nasal swab) and the second (BAL) infections (black arrows) in a representative group of other circulating SARS-CoV-2 strains (94 sequences) from the same geographical area at the time of sampling. Genomes were classified into clades using Nextclade. (C) Evolution of S protein sequences between the first and second infections compared to SARS-CoV-2 reference (SARS-CoV-2 MN908947.3). BAL, broncho-alveolar lavage; SP, signal peptide; NTD, N-terminal domain; RBD, receptor-binding domain; RBM, receptor binding motif; FP, fusion peptide; HR1/2, heptad repeat 1 and 2; TM, transmembrane domain; CP, cytoplasmic domain