FIGURE 1.
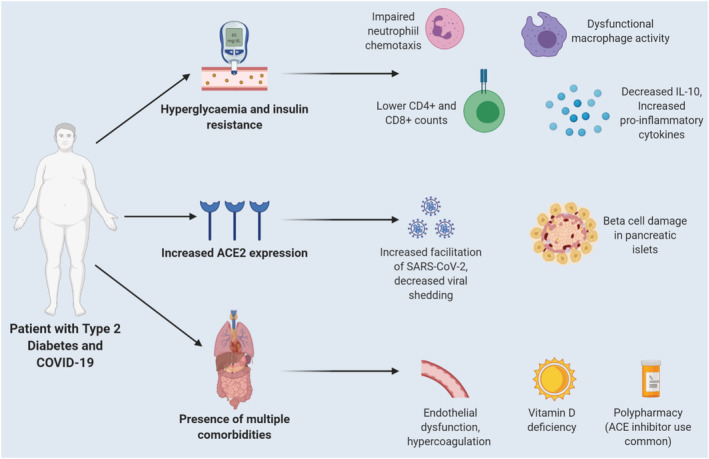
Mechanisms contributing to worsened outcomes in patients with COVID‐19 and diabetes mellitus (DM). Acute and chronic hyperglycaemia compromises the innate immune system through impaired neutrophil chemotaxis, decreased macrophage activity, dampened T‐cell responses, decreased levels of anti‐inflammatory cytokines (IL‐10) and increased proinflammatory cytokines. The increased angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression in these patients favours more efficient SARS‐CoV‐2 entry into cells and potential damage to β islet cells of the pancreas. The presence of multiple comorbidities contributes to endothelial dysfunction and hypercoagulation. Lastly, vitamin D deficiency is a common finding which can further compromise the immune system
