FIGURE 2.
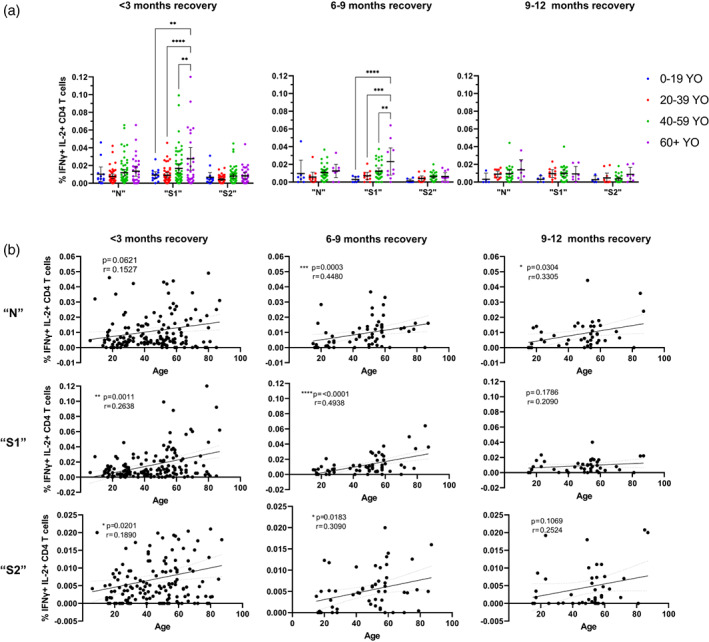
SARS‐CoV‐2‐peptide‐induced challenge responses involving dual‐responding IFNγ+ IL‐2+ CD4 T cells are persistently elevated within older individuals recovered from mild COVID‐19 for at least 9 months post recovery. (a) Comparison of the % of IFNγ+ IL‐2+ positive CD4 T cells after 6‐h incubation with SARS‐CoV‐2 peptide pools N, S1 or S2 peptide pools from individuals recovered from mild COVID‐19 less than 3 months, 6–9 months and 9–12 months post recovery from mild COVID‐19 (IgG≥1). Differences between groups were assessed using two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison test. Group <3‐month recovery 0–19 YO (years old) n = 14, 20–39 YO n = 45, 40–59 YO n = 63, 60+ YO n = 31, 6–9‐month recovery 0–19 YO n = 7, 20–39 YO n = 11, 40–59 YO n = 33, 60+ YO n = 10, 9–12 months recovery 0–19 YO n = 5, 20–39 YO n = 11, 40–59 YO n = 24, 60+ YO n = 7. (b) Correlation and simple linear regression of % of IFNγ+ IL‐2+ CD4 T cells after SARS‐CoV‐2 peptide N, S1 and S2 challenge against age in individuals recovered from mild COVID‐19 < 3‐month post recovery n = 122, 6–9‐month post recovery n = 60 and 9–12‐month post recovery n = 43. Linear regression shown with 95% confidence intervals and effect of age analysed via two‐tailed nonparametric Spearman correlation
