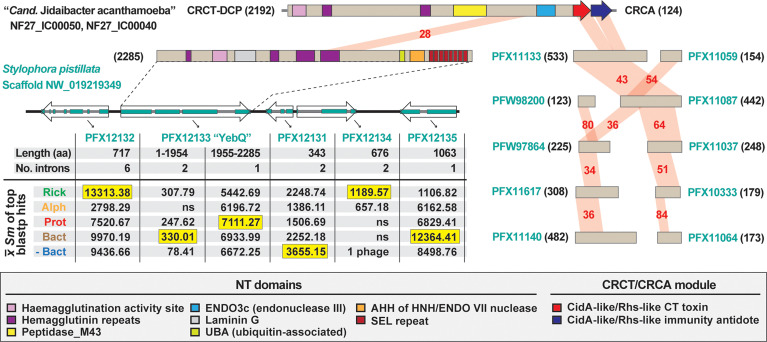
Figure 4.
The mobile nature of CRCT/CRCA modules captured in a eukaryotic genome assembly. In blastp searches against the NCBI “non-bacteria” database, the CRCT/CRCA module of “Candidatus Jidaibacter acanthamoeba” str. UWC36 consistently hit only predicted proteins from the smooth cauliflower coral (Stylophora pistillata) genome. Left, the large N-terminal region of NF27_IC00050 is similar to a large protein (PFX12133, 2285 aa) encoded on a five-gene S. pistillata scaffold (NW_019219349). PFX12133 domain architecture (descriptions in gray inset at bottom) is reminiscent of large, multi-domain hemagglutinin-like RHS toxins that may or may not carry CRCT domains (see Figures 2 , 3 ). The HaloBlast profile of PFX12133 and adjacent proteins indicates either rampant bacterial gene incorporation into the S. pistillata genome or mis-assembly of bacterial sequencing reads from S. pistillata-associated microbes. See text and Figure 2 legend for description of HaloBlast. PFX12132: stomatin-like protein 2, mitochondrial; PFX12133: uncharacterized protein YbeQ; PFX12133: uncharacterized protein YqaJ; PFX12133: hypothetical protein AWC38_SpisGene23959; PFX12135: DNA polymerase I. Right, the complete or partial CRCT/CRCA module was detected in ten smaller predicted S. pistillata proteins encoded by genes on scaffolds not incorporated into the S. pistillata assembly.