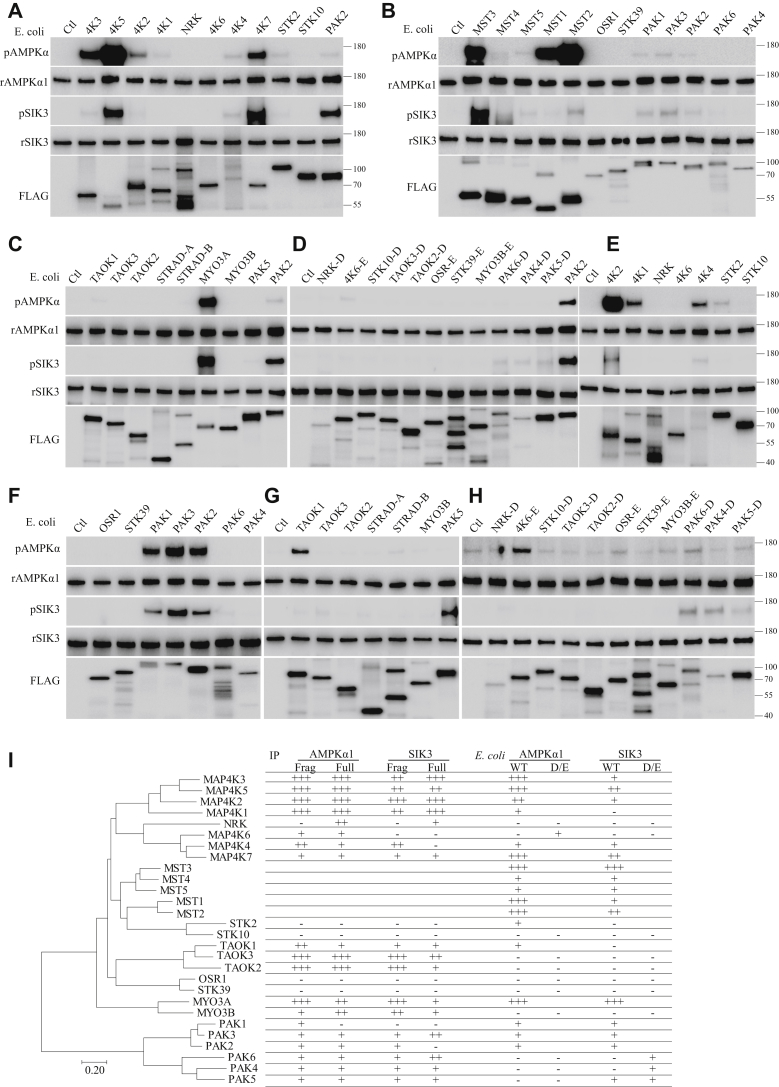
Figure 7.
Phosphorylation of AMPKα1 and SIK3 by STE20-like kinases purified from Escherichia coli. A–C, full length or fragments of STE20-like kinases tagged with the FLAG epitope (Figs. S6 and S7) were individually expressed in and purified from E. coli before being assayed with recombinant SIK3 and AMPKα1. Kinases were aligned similar to the evolutionary tree (I). D and H, for STE20 kinases whose WT forms were unable to phosphorylate SIK3 and AMPKα1, recombinant proteins with S to D or T to E mutations were expressed in and purified from E. coli before being tested for their activities on SIK3 and AMPKα1. Signals in (D) can be compared with those in (A) by referencing to PAK2. E–H, exposure time in these panels was increased over those in (A–C) to allow for detection of weak signals. Signals in (E) can be compared with those in (A) by referencing MAP4K2. Signals in (F) can be compared with those in (A) by referencing PAK2. Signals in (G) can be compared with those in (C) by referencing TAOK1. I, summary of AMPKα1 and SIK3 phosphorylation by STE20 kinases, in the phylogeny tree of the latter. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; SIK3, salt-inducible kinase 3; STE20, sterile 20.