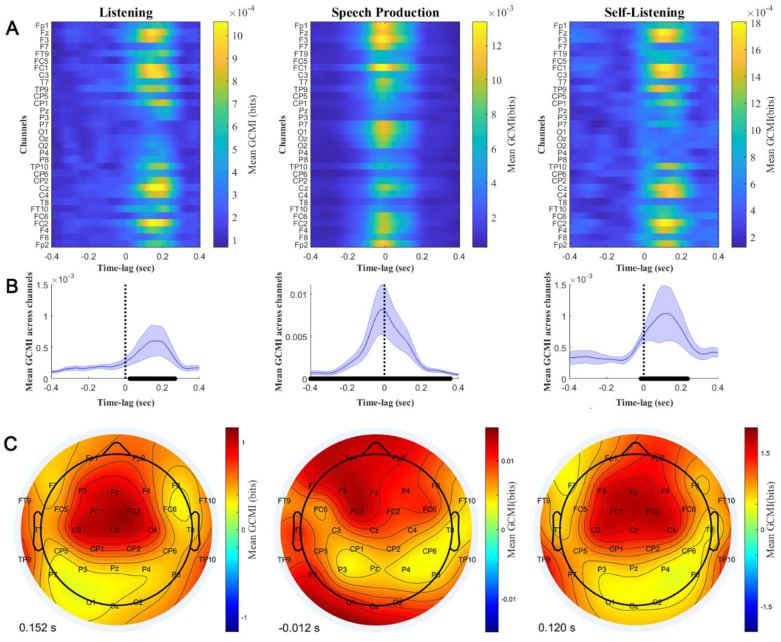
Fig. 2.
Mean lagged speech envelope tracking estimated at the scalp-level and grouped by condition. Negative times indicate the audio signal preceding the EEG signal and positive lags indicate that the brain activity follows the auditory signal. Zero lag is when the auditory and EEG signals are synchronous. Each column represents a condition. Panel A contains the channel-time-lag representation of the sample average. Colour scale represents the magnitude of the GCMI value (bits). Panel B contains the mean (blue line) and standard deviation (blue shadowed area) when collapsing across channels. The black dots on the x-axis indicate the lags in which the GCMI values are increased (95% of confidence). Panel C contains the response topography at the latency showing the maximum GCMI value, which is indicated at the bottom. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)