Figure 2.
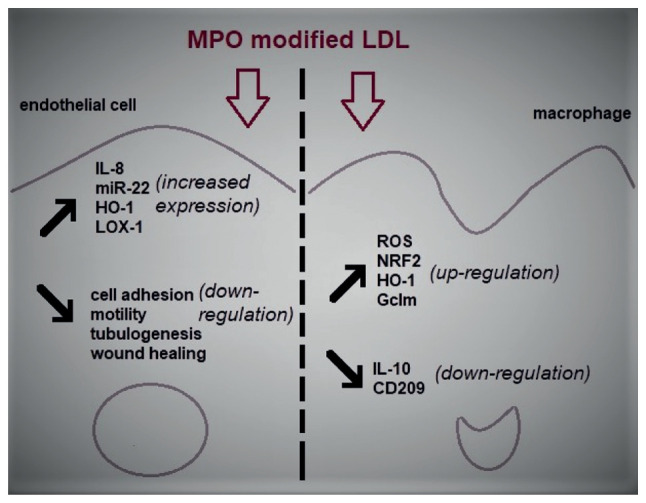
The effects of MPO modified LDL on endothelial cells and macrophage models of atherosclerosis. LDL that has been oxidized by MPO is able to induce ED which is primarily demonstrated by an increase in inflammation and a decrease in the physiological properties of ECs such as cell motility and wound healing. Similarly, Mox-LDL is responsible for the increase in oxidative stress and inflammation in macrophages through the upregulation of the generation of ROS and the downregulation of the major anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in these cells. MPO, myeloperoxidase; LDL, low-density lipoproteins; ED, endothelial dysfunction; EC, endothelial cell; Mox-LDL, MPO oxidized LDL; ROS, reactive oxygen species; miR, microRNA; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; LOX-1, lectin-like oxLDL receptor-1; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Gclm, glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit.
