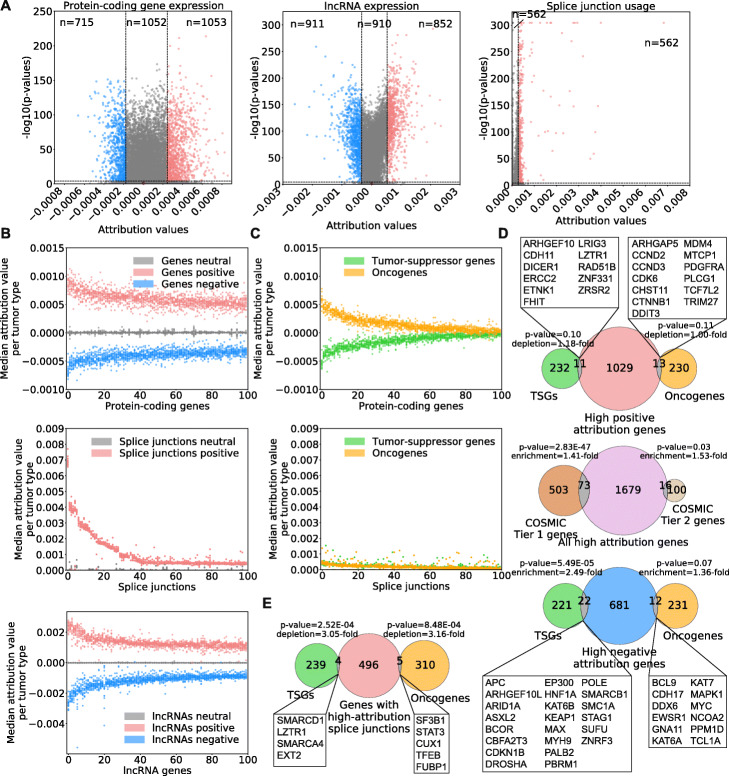
Fig. 2.
A Selection of high-attribution features from models trained with protein-coding gene expression, lncRNA gene expression or splice junction usage. Dotted lines show cutoffs used; purple points around coordinates (0,0) show features selected in neutral sets. B Median attribution values of 100 protein-coding genes, lncRNAs or splice junctions with the highest positive and negative attributions across tumor tissues. C Median attribution values of genes associated with cancer from the COSMIC database. D Overlap between COSMIC oncogenes and TSGs, and genes with high positive (top panel) or negative (bottom panel) attribution values, or between COSMIC tier 1 genes (high confidence for causal role in cancer) and tier 2 genes (some evidence of causal involvement in cancer), and all high-attribution genes (central panel). E Overlap between genes associated with cancer and genes harboring junctions with high attribution values. In both D and E, enrichment or depletion factors were calculated from the ratio of observed vs. expected overlapping genes between sets, and p-values were calculated using the hypergeometric test