Figure 4:
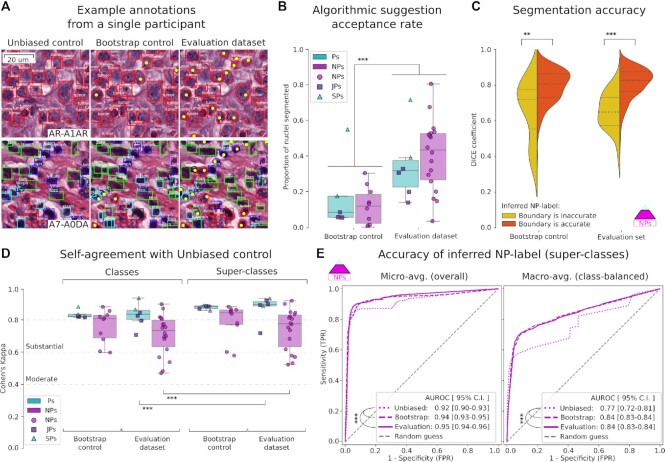
Effect of algorithmic suggestions on annotation abundance and accuracy. We compared annotations from the Evaluation dataset and controls to measure the effect of suggestions and Mask R-CNN refinement on the acquisition of nucleus segmentation data and the accuracy of annotations. A. Example annotations from a single participant. Algorithmic suggestions allow the collection of accurate nucleus segmentations without added effort. Yellow points indicate clicks to approve suggestions. B. The number of segmented nuclei clicked is significantly higher for the Evaluation dataset than for the Bootstrap control, indicating that refinement improves suggestion quality. C. Accuracy of algorithmic segmentation suggestions. The comparison is made against a limited set of manually traced segmentation boundaries obtained from 1 senior pathologist (SP). Suggestions that were determined to be correct by the expectation-maximization procedure had significantly more accurate segmentation boundaries. D. Self-agreement for annotations in the presence or absence of algorithmic suggestions. The agreement is substantial for non-pathologist (NP) and pathologist (P) groups, indicating that algorithmic suggestions do not affect classification decisions adversely. Pathologists have higher self-agreement and are less impressionable than NPs. E. ROC curves for the classification accuracy of inferred NP-label, using inferred P-truth as our reference. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.