FIG 5.
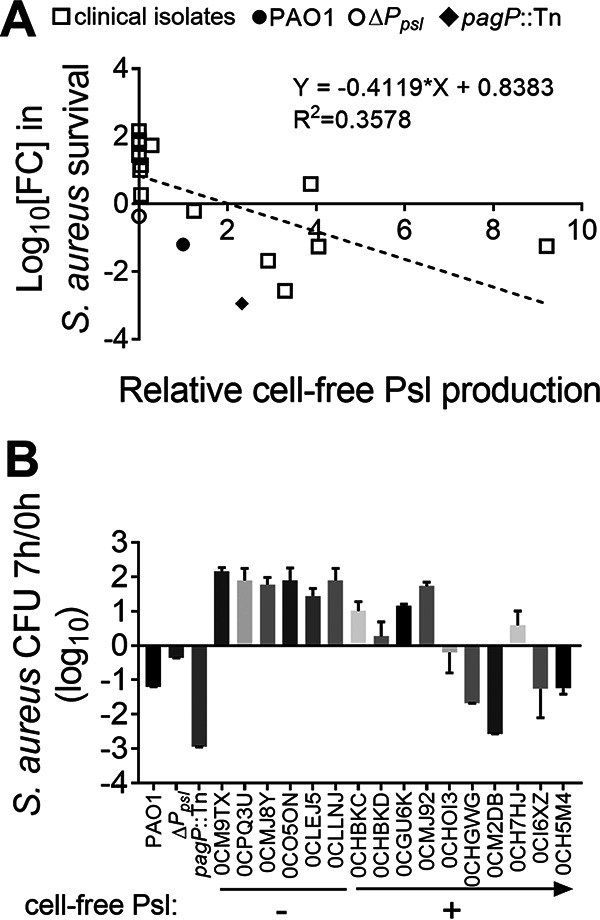
Psl production in P. aeruginosa clinical isolates positively correlates with the ability to kill S. aureus. S. aureus USA300 was cocultured with each of the 16 P. aeruginosa CF isolates, PAO1, and the ΔPpsl and pagP::Tn strains. The number of CFU at 7 h was divided by that at 0 h to quantify survival. (A) Linear regression analysis was performed to determine any correlation between the two parameters indicated. Cell-free Psl production by the designated strains was measured by immunoblot assay using Psl antibody and then normalized to PAO1. Individual points indicate biological replicates (N = 3; n = 3). (B) P. aeruginosa clinical isolates with low Psl production showed reduced S. aureus killing activity. Six of the CF isolates produced no cell-free Psl (−), while the other 10 produced variable amounts of cell-free Psl (+; the arrow indicates the increasing production of Psl), compared with that produced by PAO1. The number of CFU of S. aureus USA300 cocultured with each of the isolates, PAO1, and the ΔPpsl and pagP::Tn strains for 7 h was divided by that at 0 h to quantify S. aureus survival. Data are means and SD (N = 3; n = 3).
