Fig. 1:
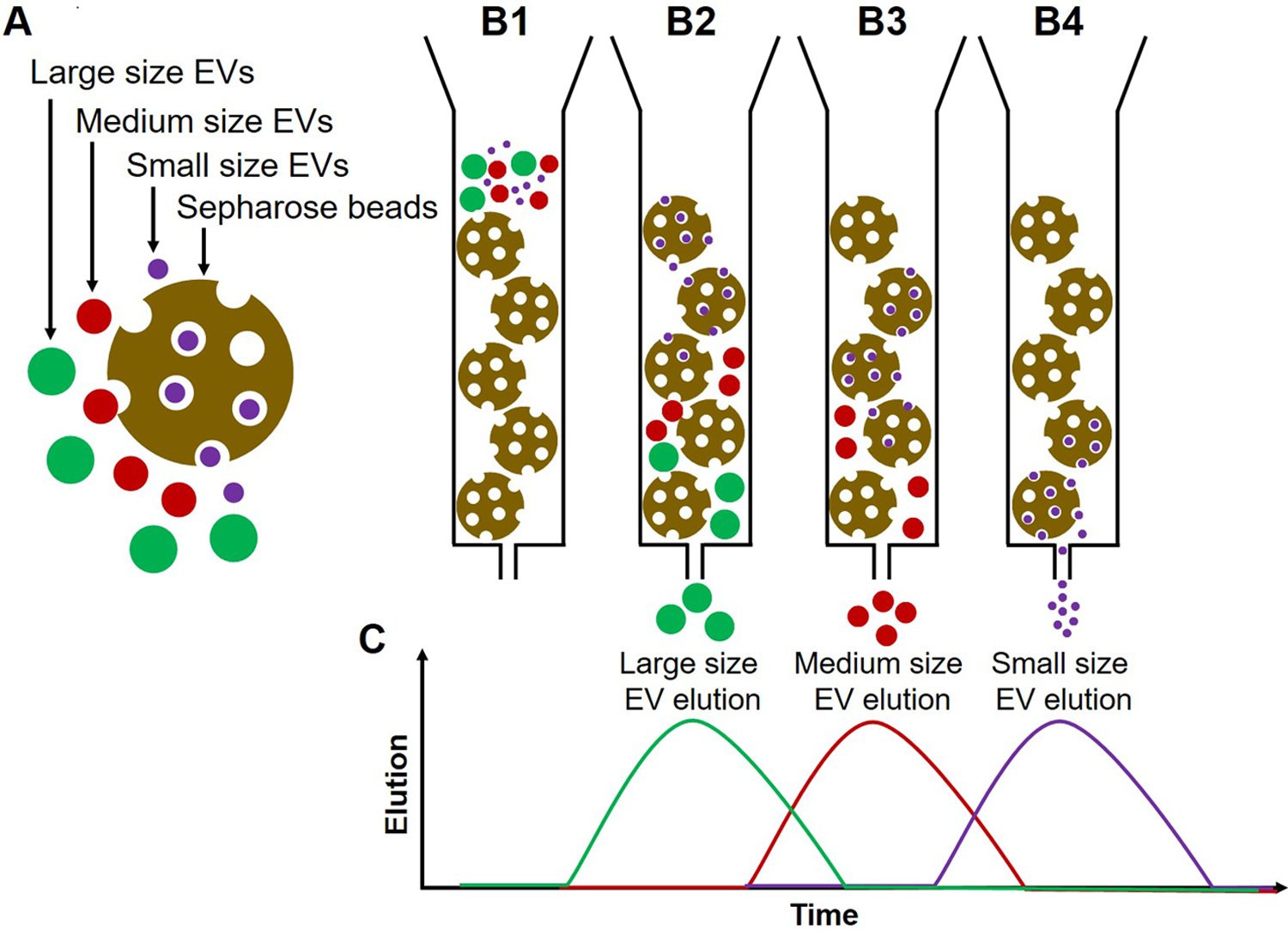
Illustration of the principle of size exclusion chromatography (SEC). (A) Sepharose beads (gold), large size EVs (green), medium-size EVs (red), and small size EVs (purple). (B1) The column is loaded with Sepharose beads and EVs are placed in the column. (B2) Larger EVs enter first into few pores of the Sepharose column, move down with the elution buffer and elute first. (B3) Medium EVs enter the pores later and thus elute after larger EVs (B4) Smaller EVs enter into many pores, move slowly through the column and elute later. (C) A histogram plot illustrating EV elution from the column; the elution time of EVs depends on their size. The vesicles elute in early fractions, while smaller protein aggregates or individual proteins are retained in the column and are eluted in later fractions.
