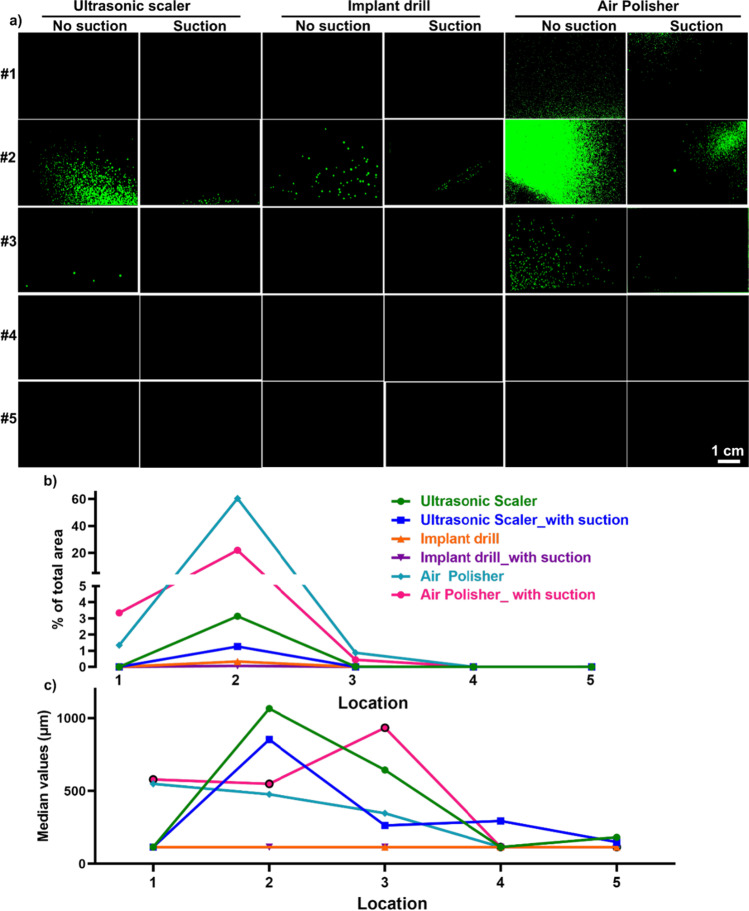
Fig. 2.
Representative images of particles on filter paper at various locations (a), the % of the total area (b), and the median particle size (c) for splatter particles. a HVS reduced splatter spread at 5 different locations: location #1 represents a right-handed dentist at 20 cm away from the source, location #2 represents a dental assistant at 15 cm away from the source, locations #3 and #4 represent the patient’s chest and body at 22 cm and 60 cm away from the source, and location #5 is at 120 cm away from the source. For locations, three dental AGPs generated the most splatter particles for a dental assistant (location 2). Among different AGPs, the air polisher generated the most splatter particles compared to the ultrasonic scaler and implant drill. b Quantification of splatters by dental AGPs by quantifying particles % of the total area for each filter paper. The application of HVS showed decreased splatter particles for all three dental AGPs. c The median size of splatter particles with and without HVS is larger than 200 μm