Figure 2. Biomaterials to modulate the lymphatic system.
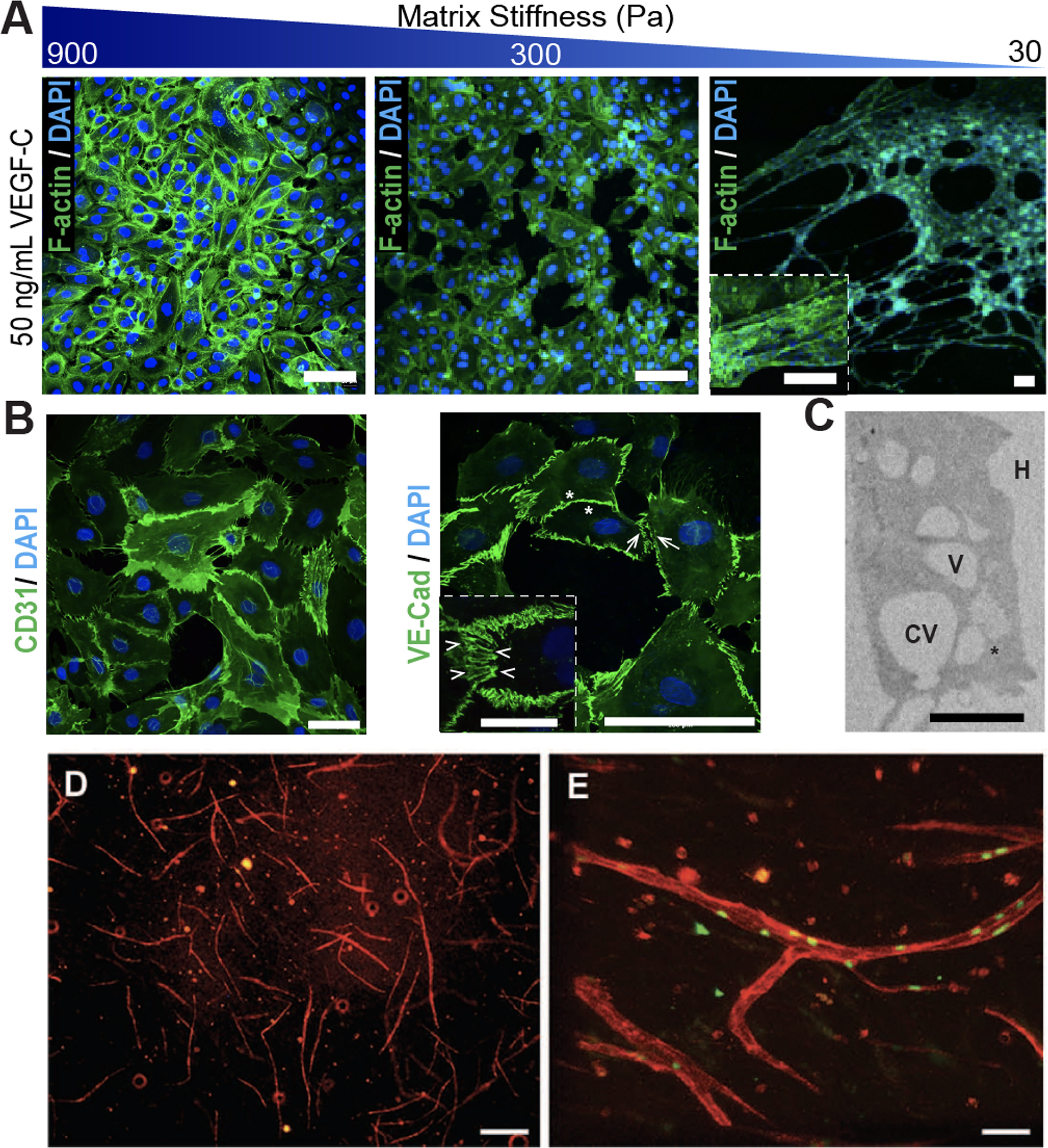
(A) Matrix stiffness of hyaluronic acid (HA)-hydrogels prime lymphatic tube formation directed by VEGF-C, as demonstrated by fluorescent microscopy of F-actin (green) and nuclei (blue). Scale bars are 50 μm. (B) Confocal images of lymphatic tubes formed on soft HA-hydrogels showing junctional markers for CD31 and VE-Cad. Enlarged rendering of confocal image stacks indicate cellular junctions (arrowheads) with discontinuous (arrows) and overlapping (asterisks) junctions. Scale bars are 50 μm and 25 μm (inset). (C) TEM analyses of lymphatic tubes formed after 12 hours showed LECs degrading the HA-hydrogels (H) to generate intracellular vacuoles (V), some of which were observed in the process of merging (asterisk) into coalescent vacuoles (CV). Scale bar is 20 μm. Illustration was adapted with permission from [26]. (D) FACS-sorted LECs mixed with 40% fibroblasts developed lymphatic capillaries (CD31, red) within Collagen type-1. (E) Lymphatic capillaries expressed the lymphatic marker Prox-1 (green). Scale bars are 40 μm. Illustration was adapted with permission from [34].
