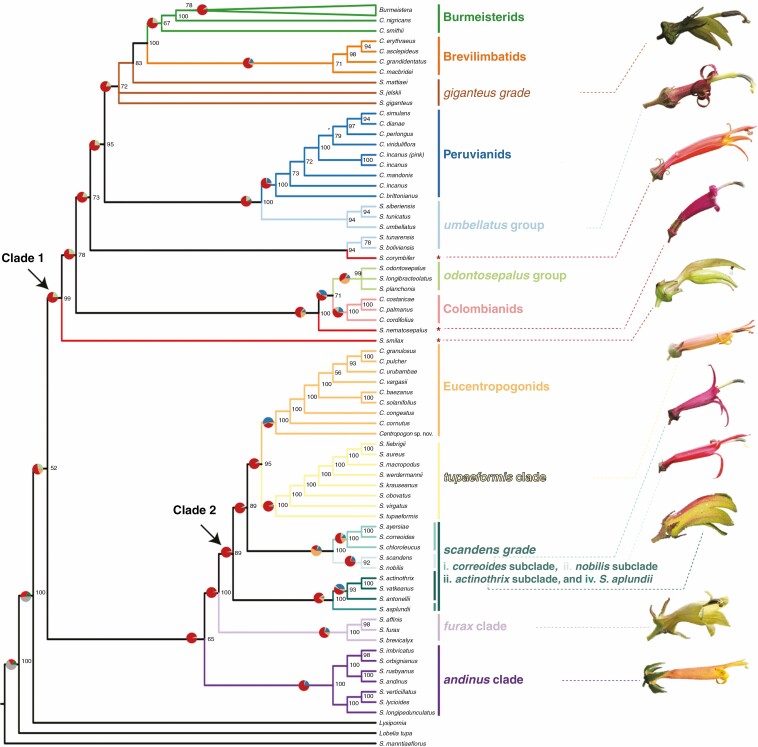
Fig. 2.
Concatenated RAxML phylogeny with informal names of closely allied species presented at the right, with the branches of the phylogeny corresponding to their members colour-coded accordingly. Names in bold text are from Lagomarsino et al. (2014) and correspond to the baccate lineages (i.e. species currently classified in Burmeistera and Centropogon). Names in italics correspond to capsular lineages (i.e. species currently classified in Siphocampylus). Individual rogue species are indicated by red asterisks. Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap support values. Pie charts above select branches illustrate gene tree discordance as estimated in PhyParts using all gene trees along the RAxML phylogeny and visualized using PhyPartsPieCharts; colours correspond to the proportion of gene trees that fall into different categories of concordance (blue: concordant genes; green: most common conflicting bipartition; red: other conflicting bipartitions; orange: gene trees with no information). Photos of living flowers from exemplar species of the Siphocampylus lineages are presented at the right. From top to bottom, these are: S. matthaei, S. tunarensis, S. corymbifer, S. nematosepalus, S. smilax, S. tupaeformis, S. correoides, S. scandens, S. actinothrix, S. affinis and S. andinus.